Disrupting microtubule network immobilizes amoeboid chemotactic receptor in the plasma membrane
- PMID: 21334306
- PMCID: PMC3079046
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2011.02.009
Disrupting microtubule network immobilizes amoeboid chemotactic receptor in the plasma membrane
Abstract
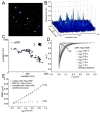
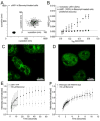
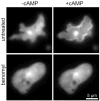
Signaling cascades are initiated in the plasma membrane via activation of one molecule by another. The interaction depends on the mutual availability of the molecules to each other and this is determined by their localization and lateral diffusion in the cell membrane. The cytoskeleton plays a very important role in this process by enhancing or restricting the possibility of the signaling partners to meet in the plasma membrane. In this study we explored the mode of diffusion of the cAMP receptor, cAR1, in the plasma membrane of Dictyostelium discoideum cells and how this is regulated by the cytoskeleton. Single-particle tracking of fluorescently labeled cAR1 using Total Internal Reflection Microscopy showed that 70% of the cAR1 molecules were mobile. These receptors showed directed motion and we demonstrate that this is not because of tracking along the actin cytoskeleton. Instead, destabilization of the microtubules abolished cAR1 mobility in the plasma membrane and this was confirmed by Fluorescence Recovery after Photobleaching. As a result of microtubule stabilization, one of the first downstream signaling events, the jump of the PH domain of CRAC, was decreased. These results suggest a role for microtubules in cAR1 dynamics and in the ability of cAR1 molecules to interact with their signaling partners.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
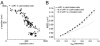
References
-
- Pierce KL, Premont RT, Lefkowitz RJ. Seven-transmembrane receptors. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002;3:639–650. - PubMed
-
- Sun Y, McGarrigle D, Huang XY. When a G protein-coupled receptor does not couple to a G protein. Mol Biosyst. 2007;3:849–854. - PubMed
-
- Milne JL, Wu L, Caterina MJ, Devreotes PN. Seven helix cAMP receptors stimulate Ca2+ entry in the absence of functional G proteins in Dictyostelium. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:5926–5931. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

