Temporal profile of Src, SSeCKS, and angiogenic factors after focal cerebral ischemia: correlations with angiogenesis and cerebral edema
- PMID: 21334414
- PMCID: PMC3100427
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuint.2011.02.014
Temporal profile of Src, SSeCKS, and angiogenic factors after focal cerebral ischemia: correlations with angiogenesis and cerebral edema
Abstract
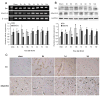
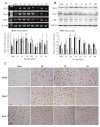
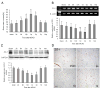
A better understanding of the underlying mechanisms of angiogenesis and vascular permeability is necessary for the development of therapeutic strategies for ischemic injury. The purpose of this study was to examine the spatial and temporal expression of Src and Src-suppressed C kinase substrate (SSeCKS) in brain after middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) and elucidate the relationships among Src, SSeCKS, and the key angiogenic factors present after stroke. Rats were subjected to either MCAO or sham operation. Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction and Western blotting results revealed that Src gradually increased starting as early as 2 h after MCAO and remained high for 1 day. In contrast, SSeCKS decreased after MCAO. Src expression correlated positively with that of vascular endothelial growth factor and angiopoietin-2, and negatively with that of SSeCKS, angiopoietin-1, and zonula occludens-1. However, SSeCKS had the reverse correlations. Changes in the expression of these factors correlated with the progress of angiogenesis and cerebral edema. Dynamic temporal changes in Src and SSeCKS expression may modulate angiogenesis and cerebral edema formation after focal cerebral ischemia.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Src regulates angiogenic factors and vascular permeability after focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion.Neuroscience. 2014 Mar 14;262:118-28. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.12.060. Epub 2014 Jan 8. Neuroscience. 2014. PMID: 24412374 Free PMC article.
-
SSeCKS regulates angiogenesis and tight junction formation in blood-brain barrier.Nat Med. 2003 Jul;9(7):900-6. doi: 10.1038/nm889. Nat Med. 2003. PMID: 12808449
-
[Expression and function of vascular endothelial growth factor and angiopoietins in rat brain after cerebral ischemia].Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2011 Dec;40(12):834-9. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 22336210 Chinese.
-
SSeCKS/Gravin/AKAP12 attenuates expression of proliferative and angiogenic genes during suppression of v-Src-induced oncogenesis.BMC Cancer. 2006 Apr 25;6:105. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-6-105. BMC Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16638134 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of SRC suppressed C kinase substrate in rat neural tissues during inflammation.Neurochem Res. 2014 Apr;39(4):748-57. doi: 10.1007/s11064-014-1265-7. Epub 2014 Mar 13. Neurochem Res. 2014. PMID: 24623461
Cited by
-
PGE2 receptor agonist misoprostol protects brain against intracerebral hemorrhage in mice.Neurobiol Aging. 2015 Mar;36(3):1439-50. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2014.12.029. Epub 2015 Jan 3. Neurobiol Aging. 2015. PMID: 25623334 Free PMC article.
-
Hemorrhagic Transformation after Tissue Plasminogen Activator Reperfusion Therapy for Ischemic Stroke: Mechanisms, Models, and Biomarkers.Mol Neurobiol. 2015 Dec;52(3):1572-1579. doi: 10.1007/s12035-014-8952-x. Epub 2014 Nov 4. Mol Neurobiol. 2015. PMID: 25367883 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electroacupuncture treatment improves neurological function associated with regulation of tight junction proteins in rats with cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014;2014:989340. doi: 10.1155/2014/989340. Epub 2014 Jun 10. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014. PMID: 25009574 Free PMC article.
-
Angiogenesis after ischemic stroke.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2023 Jul;44(7):1305-1321. doi: 10.1038/s41401-023-01061-2. Epub 2023 Feb 24. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2023. PMID: 36829053 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoxic preconditioning stimulates angiogenesis in ischemic penumbra after acute cerebral infarction.Neural Regen Res. 2013 Nov 5;8(31):2895-903. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2013.31.002. Neural Regen Res. 2013. PMID: 25206610 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akiyama C, Yuguchi T, Nishio M, Tomishima T, Fujinaka T, Taniguchi M, Nakajima Y, Kohmura E, Yoshimine T. Src family kinase inhibitor PP1 reduces secondary damage after spinal cord compression in rats. J Neurotrauma. 2004;21:923–931. - PubMed
-
- Brown MT, Cooper JA. Regulation, substrates and functions of src. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1996;1287:121–149. - PubMed
-
- Carmeliet P. Angiogenesis in health and disease. Nat Med. 2003;9:653–660. - PubMed
-
- Conway EM, Collen D, Carmeliet P. Molecular mechanisms of blood vessel growth. Cardiovasc Res. 2001;49:507–521. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

