Temporal profile of Src, SSeCKS, and angiogenic factors after focal cerebral ischemia: correlations with angiogenesis and cerebral edema
- PMID: 21334414
- PMCID: PMC3100427
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuint.2011.02.014
Temporal profile of Src, SSeCKS, and angiogenic factors after focal cerebral ischemia: correlations with angiogenesis and cerebral edema
Abstract
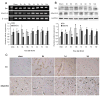
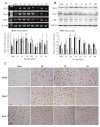
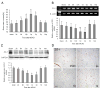
A better understanding of the underlying mechanisms of angiogenesis and vascular permeability is necessary for the development of therapeutic strategies for ischemic injury. The purpose of this study was to examine the spatial and temporal expression of Src and Src-suppressed C kinase substrate (SSeCKS) in brain after middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) and elucidate the relationships among Src, SSeCKS, and the key angiogenic factors present after stroke. Rats were subjected to either MCAO or sham operation. Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction and Western blotting results revealed that Src gradually increased starting as early as 2 h after MCAO and remained high for 1 day. In contrast, SSeCKS decreased after MCAO. Src expression correlated positively with that of vascular endothelial growth factor and angiopoietin-2, and negatively with that of SSeCKS, angiopoietin-1, and zonula occludens-1. However, SSeCKS had the reverse correlations. Changes in the expression of these factors correlated with the progress of angiogenesis and cerebral edema. Dynamic temporal changes in Src and SSeCKS expression may modulate angiogenesis and cerebral edema formation after focal cerebral ischemia.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Akiyama C, Yuguchi T, Nishio M, Tomishima T, Fujinaka T, Taniguchi M, Nakajima Y, Kohmura E, Yoshimine T. Src family kinase inhibitor PP1 reduces secondary damage after spinal cord compression in rats. J Neurotrauma. 2004;21:923–931. - PubMed
-
- Brown MT, Cooper JA. Regulation, substrates and functions of src. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1996;1287:121–149. - PubMed
-
- Carmeliet P. Angiogenesis in health and disease. Nat Med. 2003;9:653–660. - PubMed
-
- Conway EM, Collen D, Carmeliet P. Molecular mechanisms of blood vessel growth. Cardiovasc Res. 2001;49:507–521. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

