Calcitonin gene-related peptide inhibits chemokine production by human dermal microvascular endothelial cells
- PMID: 21334428
- PMCID: PMC3081395
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2011.02.007
Calcitonin gene-related peptide inhibits chemokine production by human dermal microvascular endothelial cells
Abstract
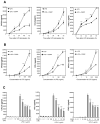
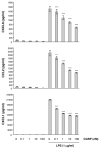
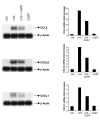
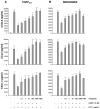
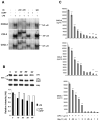
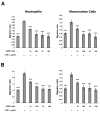
This study examined whether the sensory neuropeptide calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) inhibits release of chemokines by dermal microvascular endothelial cells. Dermal blood vessels are associated with nerves containing CGRP, suggesting that CGRP-containing nerves may regulate cutaneous inflammation through effects on vessels. We examined CGRP effects on stimulated chemokine production by a human dermal microvascular endothelial cell line (HMEC-1) and primary human dermal microvascular endothelial cells (pHDMECs). HMEC-1 cells and pHDMECs expressed mRNA for components of the CGRP and adrenomedullin receptors and CGRP inhibited LPS-induced production of the chemokines CXCL8, CCL2, and CXCL1 by both HMEC-1 cells and pHDMECs. The receptor activity-modifying protein (RAMP)1/calcitonin receptor-like receptor (CL)-specific antagonists CGRP₈-₃₇ and BIBN4096BS, blocked this effect of CGRP in a dose-dependent manner. CGRP prevented LPS-induced IκBα degradation and NF-κB binding to the promoters of CXCL1, CXCL8 and CCL2 in HMEC-1 cells and Bay 11-7085, an inhibitor of NF-κB activation, suppressed LPS-induced production of CXCL1, CXCL8 and CCL2. Thus, the NF-κB pathway appears to be involved in CGRP-mediated suppression of chemokine production. Accordingly, CGRP treatment of LPS-stimulated HMEC-1 cells inhibited their ability to chemoattract human neutrophils and mononuclear cells. Elucidation of this pathway may suggest new avenues for therapeutic manipulation of cutaneous inflammation.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The senior author was the principal investigator in the research agreement with Clinique Laboratories, LLC that funded part of this work. Clinique Laboratories, LLC provided other funds to the Department of Dermatology and the Weill Cornell Medical College.
Figures
References
-
- Ades EW, Candal FJ, Swerlick RA, George VG, Summers S, Bosse DC, Lawley TJ. HMEC-1: establishment of an immortalized human microvascular endothelial cell line. J Invest Dermatol. 1992;99:683–690. - PubMed
-
- Amano H, Negishi I, Akiyama H, Ishikawa O. Psychological stress can trigger atopic dermatitis in NC/Nga mice: An inhibitory effect of corticotropin-releasing factor. Neuropsychophrmacology. 2008;33:566–573. - PubMed
-
- Amara SG, Jonas V, Rosenfeld MG, Ong ES, Evans RM. Alternative RNA processing in calcitonin gene expression generates mRNAs encoding different polypeptide products. Nature. 1982;298:240–244. - PubMed
-
- Anisowicz A, Messineo M, Lee SW, Sager R. An NF-κB-like transcription factor mediates IL-1/TNFα induction of gro in human fibroblasts. J Immunol. 1991;147:520–527. - PubMed
-
- Arndt J, Smith N, Tausk F. Stress and atopic dermatitis. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2008;8:312–317. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

