Postoperative acute kidney injury is associated with hemoglobinemia and an enhanced oxidative stress response
- PMID: 21334433
- PMCID: PMC3090463
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.02.011
Postoperative acute kidney injury is associated with hemoglobinemia and an enhanced oxidative stress response
Abstract
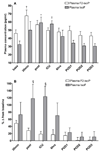
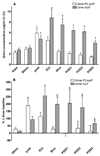
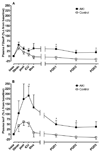
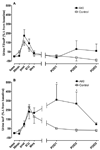
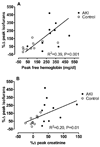
Acute kidney injury (AKI) frequently afflicts patients undergoing cardiopulmonary bypass and independently predicts death. Both hemoglobinemia and myoglobinemia are independent predictors of postoperative AKI. Release of free hemeproteins into the circulation is known to cause oxidative injury to the kidneys. This study tested the hypothesis that postoperative AKI is associated with both enhanced intraoperative hemeprotein release and increased lipid peroxidation assessed by measuring F₂-isoprostanes and isofurans. In a case-control study nested within an ongoing randomized trial of perioperative statin treatment and AKI, we compared levels of F₂-isoprostanes and isofurans with plasma levels of free hemoglobin and myoglobin in 10 cardiac surgery AKI patients to those of 10 risk-matched controls. Peak plasma free hemoglobin concentrations were significantly higher in AKI subjects (289.0 ± 37.8 versus 104.4 ± 36.5mg/dl, P = 0.01), whereas plasma myoglobin concentrations were similar between groups. The change in plasma F₂-isoprostane and isofuran levels (repeated-measures ANOVA, P = 0.02 and P = 0.001, respectively) as well as the change in urine isofuran levels (P = 0.04) was significantly greater in AKI subjects. In addition, change in peak plasma isofuran levels correlated not only with peak free plasma hemoglobin concentrations (r² = 0.39, P = 0.001) but also with peak change in serum creatinine (r² = 0.20, P = 0.01). Postoperative AKI is associated with both enhanced intraoperative hemeprotein release and enhanced lipid peroxidation. The correlations among hemoglobinemia, lipid peroxidation, and AKI indicate a potential role for hemeprotein-induced oxidative damage in the pathogenesis of postoperative AKI.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00791648.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Karkouti K, Wijeysundera DN, Yau TM, Callum JL, Cheng DC, Crowther M, Dupuis J-Y, Fremes SE, Kent B, Laflamme C, Lamy A, Legare J-F, Mazer CD, McCluskey SA, Rubens FD, Sawchuk C, Beattie WS. Acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery: focus on modifiable risk factors. Circulation. 2009;119:495–502. - PubMed
-
- Rosner MH, Okusa MD. Acute kidney injury associated with cardiac surgery. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;1:19–32. - PubMed
-
- Haase M, Bellomo R, Haase-Fielitz A. Novel biomarkers, oxidative stress, and the role of labile iron toxicity in cardiopulmonary bypass-associated acute kidney injury. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;55:2024–2033. - PubMed
-
- Mack MJ, Pfister A, Bachand D, Emery R, Magee MJ, Connolly M, Subramanian V. Comparison of coronary bypass surgery with and without cardiopulmonary bypass in patients with multivessel disease. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2004;127:167–173. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

