Stable kinesin and dynein assemblies drive the axonal transport of mammalian prion protein vesicles
- PMID: 21335237
- PMCID: PMC3576050
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.01.021
Stable kinesin and dynein assemblies drive the axonal transport of mammalian prion protein vesicles
Abstract
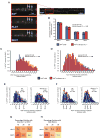
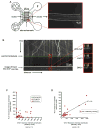
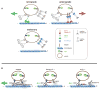
Kinesin and dynein are opposite-polarity microtubule motors that drive the tightly regulated transport of a variety of cargoes. Both motors can bind to cargo, but their overall composition on axonal vesicles and whether this composition directly modulates transport activity are unknown. Here we characterize the intracellular transport and steady-state motor subunit composition of mammalian prion protein (PrP(C)) vesicles. We identify Kinesin-1 and cytoplasmic dynein as major PrP(C) vesicle motor complexes and show that their activities are tightly coupled. Regulation of normal retrograde transport by Kinesin-1 is independent of dynein-vesicle attachment and requires the vesicle association of a complete Kinesin-1 heavy and light chain holoenzyme. Furthermore, motor subunits remain stably associated with stationary as well as with moving vesicles. Our data suggest a coordination model wherein PrP(C) vesicles maintain a stable population of associated motors whose activity is modulated by regulatory factors instead of by structural changes to motor-cargo associations.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Borchelt DR, Davis J, Fischer M, Lee MK, Slunt HH, Ratovitsky T, Regard J, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Sisodia SS, et al. A vector for expressing foreign genes in the brains and hearts of transgenic mice. Genet Anal. 1996;13:159–163. - PubMed
-
- Borchelt DR, Koliatsos VE, Guarnieri M, Pardo CA, Sisodia SS, Price DL. Rapid anterograde axonal transport of the cellular prion glycoprotein in the peripheral and central nervous systems. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:14711–14714. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

