Effect of continuous glucose monitoring on hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 21335621
- PMCID: PMC3064030
- DOI: 10.2337/dc10-1989
Effect of continuous glucose monitoring on hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes
Abstract
Objective: To assess the impact of continuous glucose monitoring on hypoglycemia in people with type 1 diabetes.
Research design and methods: In this randomized, controlled, multicenter study, 120 children and adults on intensive therapy for type 1 diabetes and a screening level of glycated hemoglobin A(1c) (HbA(1c)) <7.5% were randomly assigned to a control group performing conventional home monitoring with a blood glucose meter and wearing a masked continuous glucose monitor every second week for five days or to a group with real-time continuous glucose monitoring. The primary outcome was the time spent in hypoglycemia (interstitial glucose concentration <63 mg/dL) over a period of 26 weeks. Analysis was by intention to treat for all randomized patients.
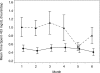
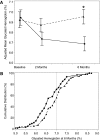
Results: The time per day spent in hypoglycemia was significantly shorter in the continuous monitoring group than in the control group (mean ± SD 0.48 ± 0.57 and 0.97 ± 1.55 h/day, respectively; ratio of means 0.49; 95% CI 0.26-0.76; P = 0.03). HbA(1c) at 26 weeks was lower in the continuous monitoring group than in the control group (difference -0.27%; 95% CI -0.47 to -0.07; P = 0.008). Time spent in 70 to 180 mg/dL normoglycemia was significantly longer in the continuous glucose monitoring group compared with the control group (mean hours per day, 17.6 vs. 16.0, P = 0.009).
Conclusions: Continuous glucose monitoring was associated with reduced time spent in hypoglycemia and a concomitant decrease in HbA(1c) in children and adults with type 1 diabetes.
Figures
Comment in
-
Continuous glucose monitoring in children and adults with well-controlled type 1 diabetes reduces hypoglycaemia.Evid Based Med. 2012 Feb;17(1):18-9. doi: 10.1136/ebm-2011-100076. Epub 2011 Jul 29. Evid Based Med. 2012. PMID: 21803761 No abstract available.
References
-
- The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 1993;329:977–986 - PubMed
-
- Hanberger L, Samuelsson U, Lindblad B, Ludvigsson J, Swedish Childhood Diabetes Registry SWEDIABKIDS A1C in children and adolescents with diabetes in relation to certain clinical parameters: the Swedish Childhood Diabetes Registry SWEDIABKIDS. Diabetes Care 2008;31:927–929 - PubMed
-
- Shalitin S, Phillip M. Hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes: a still unresolved problem in the era of insulin analogs and pump therapy. Diabetes Care 2008;31(Suppl. 2):S121–S124 - PubMed
-
- Cryer PE. Hypoglycaemia: the limiting factor in the glycaemic management of type I and type II diabetes. Diabetologia 2002;45:937–948 - PubMed
-
- Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group Effect of intensive diabetes treatment on the development and progression of long-term complications in adolescents with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. J Pediatr 1994;125:177–188 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

