Incidence, risk factors, and outcomes of acute kidney injury after pediatric cardiac surgery: a prospective multicenter study
- PMID: 21336114
- PMCID: PMC3286600
- DOI: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31821201d3
Incidence, risk factors, and outcomes of acute kidney injury after pediatric cardiac surgery: a prospective multicenter study
Abstract
Objective: To determine the incidence, severity, and risk factors of acute kidney injury in children undergoing cardiac surgery for congenital heart defects.
Design: Prospective observational multicenter cohort study.
Setting: Three pediatric intensive care units at academic centers.
Patients: Three hundred eleven children between the ages of 1 month and 18 yrs undergoing pediatric cardiac surgery.
Interventions: None.
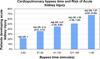
Measurements and main results: Acute kidney injury was defined as a ≥50% increase in serum creatinine from the preoperative value. Secondary outcomes were length of mechanical ventilation, length of intensive care unit and hospital stays, acute dialysis, and in-hospital mortality. The cohort had an average age of 3.8 yrs and was 45% women and mostly white (82%). One-third had prior cardiothoracic surgery, 91% of the surgeries were elective, and almost all patients required cardiopulmonary bypass. Acute kidney injury occurred in 42% (130 patients) within 3 days after surgery. Children ≥2 yrs old and <13 yrs old had a 72% lower likelihood of acute kidney injury (adjusted odds ratio: 0.28, 95% confidence interval: 0.16, 0.48), and patients 13 yrs and older had 70% lower likelihood of acute kidney injury (adjusted odds ratio: 0.30, 95% confidence interval: 0.10, 0.88) compared to patients <2 yrs old. Longer cardiopulmonary bypass time was linearly and independently associated with acute kidney injury. The development of acute kidney injury was independently associated with prolonged ventilation and with increased length of hospital stay.
Conclusions: Acute kidney injury is common after pediatric cardiac surgery and is associated with prolonged mechanical ventilation and increased hospital stay. Cardiopulmonary bypass time and age were independently associated with acute kidney injury risk. Cardiopulmonary bypass time may be a marker for case complexity.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Devarajan consulted for Abbott and Biosite, received a grant from the NIH, and is a co-inventor on the pending NGAL patent. Dr. Parikh consulted for Abbott. The remaining authors have not disclosed any potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

Comment in
-
Kidney injury in kids following bypass surgery: more to know.Crit Care Med. 2011 Jun;39(6):1596-7. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31821856f3. Crit Care Med. 2011. PMID: 21610646 No abstract available.
References
-
- Pedersen KR, Povlsen JV, Christensen S, et al. Risk factors for acute renal failure requiring dialysis after surgery for congenital heart disease in children. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2007;51:1344–1349. - PubMed
-
- Zappitelli M, Bernier PL, Saczkowski RS, et al. A small post-operative rise in serum creatinine predicts acute kidney injury in children undergoing cardiac surgery. Kidney Int. 2009;76:885–892. - PubMed
-
- Shaw NJ, Brocklebank JT, Dickinson DF, et al. Long-term outcome for children with acute renal failure following cardiac surgery. Int J Cardiol. 1991;31:161–165. - PubMed
-
- Heying R, Seghaye MC, Grabitz RG, et al. Mid-term follow-up after multiple system organ failure following cardiac surgery in children. Acta Paediatr. 1999;88:1238–1243. - PubMed
-
- Dimopoulos K, Diller GP, Koltsida E, et al. Prevalence, predictors, and prognostic value of renal dysfunction in adults with congenital heart disease. Circulation. 2008;117:2320–2328. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

