Interbilayer-crosslinked multilamellar vesicles as synthetic vaccines for potent humoral and cellular immune responses
- PMID: 21336265
- PMCID: PMC3077947
- DOI: 10.1038/nmat2960
Interbilayer-crosslinked multilamellar vesicles as synthetic vaccines for potent humoral and cellular immune responses
Abstract
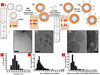
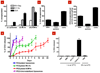
Vaccines based on recombinant proteins avoid the toxicity and antivector immunity associated with live vaccine (for example, viral) vectors, but their immunogenicity is poor, particularly for CD8(+) T-cell responses. Synthetic particles carrying antigens and adjuvant molecules have been developed to enhance subunit vaccines, but in general these materials have failed to elicit CD8(+) T-cell responses comparable to those for live vectors in preclinical animal models. Here, we describe interbilayer-crosslinked multilamellar vesicles formed by crosslinking headgroups of adjacent lipid bilayers within multilamellar vesicles. Interbilayer-crosslinked vesicles stably entrapped protein antigens in the vesicle core and lipid-based immunostimulatory molecules in the vesicle walls under extracellular conditions, but exhibited rapid release in the presence of endolysosomal lipases. We found that these antigen/adjuvant-carrying vesicles form an extremely potent whole-protein vaccine, eliciting endogenous T-cell and antibody responses comparable to those for the strongest vaccine vectors. These materials should enable a range of subunit vaccines and provide new possibilities for therapeutic protein delivery.
Figures



Comment in
-
Synthetic vaccines: Immunity without harm.Nat Mater. 2011 Mar;10(3):166-8. doi: 10.1038/nmat2977. Nat Mater. 2011. PMID: 21336292 No abstract available.
References
-
- Guy B. The perfect mix: recent progress in adjuvant research. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007;5:505–517. - PubMed
-
- Perrie Y, Mohammed AR, Kirby DJ, McNeil SE, Bramwell VW. Vaccine adjuvant systems: enhancing the efficacy of sub-unit protein antigens. Int. J. Pharm. 2008;364:272–280. - PubMed
-
- Reed SG, Bertholet S, Coler RN, Friede M. New horizons in adjuvants for vaccine development. Trends Immunol. 2009;30:23–32. - PubMed
-
- Walker BD, Burton DR. Toward an AIDS vaccine. Science. 2008;320:760–764. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

