Association of a functional variant downstream of TNFAIP3 with systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 21336280
- PMCID: PMC3103780
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.766
Association of a functional variant downstream of TNFAIP3 with systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
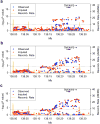
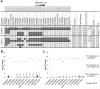
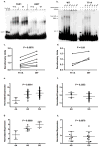
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE, MIM152700) is an autoimmune disease characterized by self-reactive antibodies resulting in systemic inflammation and organ failure. TNFAIP3, encoding the ubiquitin-modifying enzyme A20, is an established susceptibility locus for SLE. By fine mapping and genomic re-sequencing in ethnically diverse populations, we fully characterized the TNFAIP3 risk haplotype and identified a TT>A polymorphic dinucleotide (deletion T followed by a T to A transversion) associated with SLE in subjects of European (P = 1.58 × 10(-8), odds ratio = 1.70) and Korean (P = 8.33 × 10(-10), odds ratio = 2.54) ancestry. This variant, located in a region of high conservation and regulatory potential, bound a nuclear protein complex composed of NF-κB subunits with reduced avidity. Further, compared with the non-risk haplotype, the haplotype carrying this variant resulted in reduced TNFAIP3 mRNA and A20 protein expression. These results establish this TT>A variant as the most likely functional polymorphism responsible for the association between TNFAIP3 and SLE.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 AR055385/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000154/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025741/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01AR051545-01A2/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AI078004/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- N01 AR62277/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P60 AR053308/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE018209/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI063274/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000079/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AR49084/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR020143/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 GM103510/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024999/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR053483/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR-00079/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AI083790/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR015577/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 RR031152/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AR062277/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR056360/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 AR058621/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI070983/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI071651/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR048311/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR043814/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI024717/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR042460/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR033062/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA141700/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025014/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- L30 AI071651/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR43814/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR043727/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- ARC_/Arthritis Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01 CA141700/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 24717/PHS HHS/United States
- R01 AR33062/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI070304/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI083194/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AR049084/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- ULI RR025014-02/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR051545/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR043274/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AI050026/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

