Isolation and transcriptome analysis of adult zebrafish cells enriched for skeletal muscle progenitors
- PMID: 21337346
- PMCID: PMC3075361
- DOI: 10.1002/mus.21972
Isolation and transcriptome analysis of adult zebrafish cells enriched for skeletal muscle progenitors
Abstract
Introduction: Over the past 10 years, the use of zebrafish for scientific research in the area of muscle development has increased dramatically. Although several protocols exist for the isolation of adult myoblast progenitors from larger fish, no standardized protocol exists for the isolation of myogenic progenitors from adult zebrafish muscle.
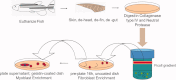
Methods: Using a variant of a mammalian myoblast isolation protocol, zebrafish muscle progenitors have been isolated from the total dorsal myotome. These zebrafish myoblast progenitors can be cultured for several passages and then differentiated into multinucleated, mature myotubes.
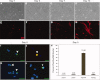
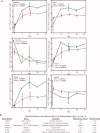
Results: Transcriptome analysis of these cells during myogenic differentiation revealed a strong downregulation of pluripotency genes, while, conversely, showing an upregulation of myogenic signaling and structural genes.
Conclusions: Together these studies provide a simple, yet detailed method for the isolation and culture of myogenic progenitors from adult zebrafish, while further promoting their therapeutic potential for the study of muscle disease and drug screening.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Lieschke GJ, Currie PD. Animal models of human disease: zebrafish swim into view. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8:353–367. - PubMed
-
- Devoto SH, Melançon E, Eisen JS, Westerfield M. Identification of separate slow and fast muscle precursor cells in vivo, prior to somite formation. Development. 1996;122:3371–3380. - PubMed
-
- Hollway GE, Bryson-Richardson RJ, Berger S, Cole NJ, Hall TE, Currie PD. Whole-somite rotation generates muscle progenitor cell compartments in the developing zebrafish embryo. Dev Cell. 2007;12:207–219. - PubMed
-
- Bassett DI, Currie PD. The zebrafish as a model for muscular dystrophy and congenital myopathy. Hum Mol Genet. 2003;12:R265–R270. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

