Effect of structural modifications on 3-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)-2,4-thiazolidinedione-induced hepatotoxicity in Fischer 344 rats
- PMID: 21337588
- PMCID: PMC3175016
- DOI: 10.1002/jat.1639
Effect of structural modifications on 3-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)-2,4-thiazolidinedione-induced hepatotoxicity in Fischer 344 rats
Abstract
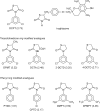
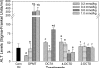
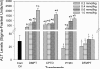
Glitazones, used for type II diabetes, have been associated with liver damage in humans. A structural feature known as a 2,4-thiazolidinedione (TZD) ring may contribute to this toxicity. TZD rings are of interest since continued human exposure via the glitazones and various prototype drugs is possible. Previously, we found that 3-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)-2,4-thiazolidinedione (DCPT) was hepatotoxic in rats. To evaluate the importance of structure on DCPT toxicity, we therefore studied two series of analogs. The TZD ring was replaced with: a mercaptoacetic acid group {[[[(3,5-dichlorophenyl)amino]carbonyl]thio]acetic acid, DCTA}; a methylated TZD ring [3-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)-5-methyl-2,4-thiazolidinedione, DPMT]; and isomeric thiazolidinone rings [3-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)-2- and 3-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)-4-thiazolidinone, 2-DCTD and 4-DCTD, respectively]. The following phenyl ring-modified analogs were also tested: 3-phenyl-, 3-(4-chlorophenyl)-, 3-(3,5-dimethylphenyl)- and 3-[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-2,4-thiazolidinedione (PTZD, CPTD, DMPT and DFMPT, respectively). Toxicity was assessed in male Fischer 344 rats 24 h after administration of the compounds. In the TZD series only DPMT produced liver damage, as evidenced by elevated serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) activities at 0.6 and 1.0 mmol kg(-1) (298.6 ± 176.1 and 327.3 ± 102.9 Sigma-Frankel units ml(-1) , respectively) vs corn oil controls (36.0 ± 11.3) and morphological changes in liver sections. Among the phenyl analogs, hepatotoxicity was observed in rats administered PTZD, CPTD and DMPT; with ALT values of 1196.2 ± 133.6, 1622.5 ± 218.5 and 2071.9 ± 217.8, respectively (1.0 mmol kg(-1) doses). Morphological examination revealed severe hepatic necrosis in these animals. Our results suggest that hepatotoxicity of these compounds is critically dependent on the presence of a TZD ring and also the phenyl substituents.
Copyright © 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures


References
-
- Ali AM, Saber GE, Mahfouz NM, El-Gendy MA, Radwan AA, Hamid MA. Synthesis and three-dimensional qualitative structure selectivity relationships of 3,5-disubstituted-2,4-thiazolidinedione derivatives as COX2 inhibitors. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2007;30:1186–1204. - PubMed
-
- Baughman TM, Graham RA, Wells-Knecht K, Silver IS, Tyler LO, Wells-Knecht M, Zhao K. Metabolic activation of pioglitazone identified from rat and human liver microsomes and freshly isolated hepatocytes. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2005;33:733–738. - PubMed
-
- Brouwer WG, Blem AR. Substituted thiazolidinones useful as plant growth regulators. #4,664,694 US patent. 1987
-
- Bruno G, Costantino L, Curinga C, Maccari R, Monforte F, Nicolo F, Ottana R, Vigorita MG. Synthesis and aldose reductase inhibitory activity of 5-arylidene-2,4-thiazolidinediones. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2002;10:1077–1084. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

