Light sheet fluorescence microscopy: a review
- PMID: 21339178
- PMCID: PMC3201139
- DOI: 10.1369/0022155410394857
Light sheet fluorescence microscopy: a review
Abstract
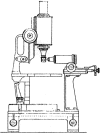
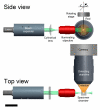
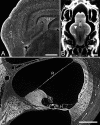
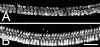
Light sheet fluorescence microscopy (LSFM) functions as a non-destructive microtome and microscope that uses a plane of light to optically section and view tissues with subcellular resolution. This method is well suited for imaging deep within transparent tissues or within whole organisms, and because tissues are exposed to only a thin plane of light, specimen photobleaching and phototoxicity are minimized compared to wide-field fluorescence, confocal, or multiphoton microscopy. LSFMs produce well-registered serial sections that are suitable for three-dimensional reconstruction of tissue structures. Because of a lack of a commercial LSFM microscope, numerous versions of light sheet microscopes have been constructed by different investigators. This review describes development of the technology, reviews existing devices, provides details of one LSFM device, and shows examples of images and three-dimensional reconstructions of tissues that were produced by LSFM.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the authorship and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Becker K, Jährling N, Kramer ER, Schnorrer F, Dodt HU. 2008. Ultramicroscopy: 3D reconstruction of large microscopical specimens. J Biophotonics. 1:36-42 - PubMed
-
- Buytaert JA, Dirckx JJ. 2007. Design and quantitative resolution measurements of an optical virtual sectioning three-dimensional imaging technique for biomedical specimens, featuring two-micrometer slicing resolution. J Biomed Opt. 12:014039. - PubMed
-
- Denk W, Strickler J, Webb W. 1990. Two-photon laser scanning fluorescence microscopy. Science. 248:73-76 - PubMed
-
- Dodt HU, Leischner U, Schierloh A, Jährling N, Mauch CP, Deininger K, Deussing JM, Eder M, Zieglgsnsberger W, Becker K. 2007. Ultramicroscopy: three-dimensional visualization of neuronal networks in the whole mouse brain. Nat Methods. 4:331-336 - PubMed
-
- Dunsby C. 2008. Optically sectioned imaging by oblique plane microscopy. Opt Express. 16:20306-20316 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

