Mechanism of microtubule-facilitated "fast track" nuclear import
- PMID: 21339293
- PMCID: PMC3077634
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.210302
Mechanism of microtubule-facilitated "fast track" nuclear import
Abstract
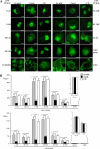
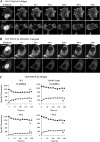
Although the microtubule (MT) cytoskeleton has been shown to facilitate nuclear import of specific cancer-regulatory proteins including p53, retinoblastoma protein, and parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTHrP), the MT association sequences (MTASs) responsible and the nature of the interplay between MT-dependent and conventional importin (IMP)-dependent nuclear translocation are unknown. Here we used site-directed mutagenesis, live cell imaging, and direct IMP and MT binding assays to map the MTAS of PTHrP for the first time, finding that it is within a short modular region (residues 82-108) that overlaps with the IMPβ1-recognized nuclear localization signal (residues 66-108) of PTHrP. Importantly, fluorescence recovery after photobleaching experiments indicated that disruption of the MT network or mutation of the MTAS of PTHrP decreases the rate of nuclear import by 2-fold. Moreover, MTAS functions depend on mutual exclusivity of binding of PTHrP to MTs and IMPβ1 such that, following MT-dependent trafficking toward the nucleus, perinuclear PTHrP can be displaced from MTs by IMPβ1 prior to import into the nucleus. This is the first molecular definition of an MTAS that facilitates protein nuclear import as well as the first delineation of the mechanism whereby cargo is transferred directly from the cytoskeleton to the cellular nuclear import apparatus. The results have broad significance with respect to fundamental processes regulating cell physiology/transformation.
Figures









References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

