Herbaceous peony (Paeonia lactiflora Pall.) as an alternative source of oleanolic and ursolic acids
- PMID: 21340006
- PMCID: PMC3039972
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms12010655
Herbaceous peony (Paeonia lactiflora Pall.) as an alternative source of oleanolic and ursolic acids
Abstract
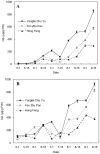
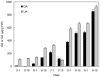
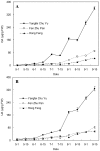
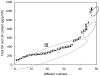
Oleanolic acid (OA) and ursolic acid (UA) have been proven to possess many biological activities, and much attention is focused on the search for plants which are rich in OA and UA. In this report, the OA and UA accumulation characteristics were investigated in 47 cultivars of Chinese herbaceous peony (Paeonia lactiflora Pall.) and were followed in three cultivars over different developmental stages as measured by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). OA and UA levels in leaves and stems demonstrated an overall upward trend from May 1 to September 15 except for UA in the leaves of "Hong Feng". The maximum values of OA and UA in leaves of "Yangfei Chu Yu", "Fen Zhu Pan" and "Hong Feng" were 852.98, 575.60, 290.48 μg/g FW and 924.94, 827.36, 432.67 μg/g FW, respectively. The maximum values of OA and UA in stems of "Yangfei Chu Yu", "Fen Zhu Pan" and "Hong Feng" were 359.28, 90.49, 43.90 μg/g FW and 326.86, 82.25, 56.63 μg/g FW, respectively. OA and UA contents in leaves of 47 different herbaceous peony cultivars ranged from 66.73-618.12 and 36.23-665.14 μg/g FW, respectively, with average values of 171.62 and 227.57 μg/g FW, respectively. The results suggested that the aboveground parts of herbaceous peony may be used as an alternative source of OA and UA for medicinal purposes in addition to its ornamental purposes.
Keywords: HPLC; Paeonia lactiflora; cultivar; oleanolic acid; ursolic acid.
Figures

References
-
- Hong DY, Pan KY. Paeoniaceae. In: Wu ZY, Raven PH, editors. Flora of China. Vol. 6. Science Press and Missouri Botanic Garden Press; Beijing, China: 2001. pp. 127–132.
-
- Braca A, Kiem PV, Yen PH, Nhiem NX, Quang TH, Cuong NX, Minh CV. New monoterpene glycosides from Paeonia lactiflora. Fitoterapia. 2008;79(2):117–120. - PubMed
-
- Kim N, Park KR, Park IS, Park YH. Application of novel HPLC method to the analysis of regional and seasonal variation of the active compounds in Paeonia lactiflor. Food Chem. 2006;96(3):496–502.
-
- Wang HB, Gu WF, Chu WJ, Zhang S, Tang XC, Qin GW. Monoterpene glucosides from Paeonia lactiflor. J Nat Prod. 2009;72(7):1321–1324. - PubMed
-
- Kumar N, Motto MG. Volatile constituents of peony flowers. Phytochemistry. 1985;25(1):250–253.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

