Combined effects of cyclooxygenase-1 and cyclooxygenase-2 selective inhibitors on ovarian carcinoma in vivo
- PMID: 21340007
- PMCID: PMC3039973
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms12010668
Combined effects of cyclooxygenase-1 and cyclooxygenase-2 selective inhibitors on ovarian carcinoma in vivo
Abstract
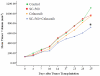
The present study was designed to investigate the combined effects of cyclooxygenase (COX)-1 and COX-2 selective inhibitors on human ovarian SKOV-3 carcinoma cells xenograft-bearing mice. The animals were treated with 3 mg/kg SC-560 (a COX-1 selective inhibitor) alone, 25 mg/kg celecoxib (a COX-2 selective inhibitor) alone, or SC-560/celecoxib by gavage, twice a day for three weeks. To test the mechanism of inhibition of tumor growth by COX selective inhibitors, the index of proliferating cells in tumor tissues was determined by immunostaining and the index of apoptotic cells by the terminal-deoxynucleotidyl-transferase-mediated deoxyuridine triphosphate nick end labeling (TUNEL) method. The inhibitory rate on tumor growth in the combination group was 35.54% which is significant statistically compared with that of the control group (P < 0.05). In the combination group, the index of cell proliferation and apoptosis were 12.40% and 51.03% respectively, which are significant statistically compared with those of the control group (22.56%, 19.07%, all P < 0.05). These studies indicate that synergism between two COX inhibitors and inhibitor combination treatment has particular potential for chemoprevention of ovarian cancer growth.
Keywords: apoptosis; cell proliferation; cyclooxygenase selective inhibitor; mice; ovarian carcinoma.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Antitumor properties of taxol in combination with cyclooxygenase-1 and cyclooxygenase-2 selective inhibitors on ovarian tumor growth in vivo.Oncol Res. 2012;20(2-3):49-59. doi: 10.3727/096504012x13473664562466. Oncol Res. 2012. PMID: 23193911
-
Effects of cyclooxygenase inhibitors in combination with taxol on expression of cyclin D1 and Ki-67 in a xenograft model of ovarian carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(8):9741-9753. doi: 10.3390/ijms13089741. Epub 2012 Aug 3. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22949827 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of a cyclooxygenase-1-selective inhibitor in a mouse model of ovarian cancer, administered alone or in combination with ibuprofen, a nonselective cyclooxygenase inhibitor.Med Oncol. 2009;26(2):170-7. doi: 10.1007/s12032-008-9104-9. Epub 2008 Nov 6. Med Oncol. 2009. PMID: 18988002
-
Celecoxib: a potent cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor in cancer prevention.Cancer Detect Prev. 2004;28(2):127-42. doi: 10.1016/j.cdp.2003.12.005. Cancer Detect Prev. 2004. PMID: 15068837 Review.
-
COX-2 inhibition and lung cancer.Semin Oncol. 2004 Apr;31(2 Suppl 7):45-52. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2004.03.045. Semin Oncol. 2004. PMID: 15179623 Review.
Cited by
-
All-trans retinoic acid treatment is associated with prohibitin expression in renal interstitial fibrosis rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(3):2769-2782. doi: 10.3390/ijms13032769. Epub 2012 Mar 1. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22489124 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Eicosanoids in Gynecological Malignancies.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Aug 26;11:1233. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.01233. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32982722 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bufalin induces lung cancer cell apoptosis via the inhibition of PI3K/Akt pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(2):2025-2035. doi: 10.3390/ijms13022025. Epub 2012 Feb 14. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22408435 Free PMC article.
-
Combined use of COX-1 and VEGF immunohistochemistry refines the histopathologic prognosis of renal cell carcinoma.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Jul 1;8(7):8165-77. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26339385 Free PMC article.
-
Less expression of prohibitin is associated with increased paired box 2 (PAX2) in renal interstitial fibrosis rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(8):9808-9825. doi: 10.3390/ijms13089808. Epub 2012 Aug 6. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22949832 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ozols RF. Recurrent ovarian cancer: evidence-based treatment. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002;20:1161–1163. - PubMed
-
- Dannenberg AJ, Subbaramaiah K. Targeting cyclooxygenase-2 in human neoplasia: rationale and promise. Cancer Cell. 2003;4:431–436. - PubMed
-
- Gupta RA, Dubois RN. Colorectal cancer prevention and treatment by inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2. Nat. Rev Cancer. 2001;1:11–21. - PubMed
-
- Smith WL, Garavito RM, DeWitt DL. Prostaglandin endoperoxide H synthases (cyclooxygenases)-1 and -2. J. Biol. Chem. 1996;271:33157–33160. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

