Poly(diol-co-citrate)s as novel elastomeric perivascular wraps for the reduction of neointimal hyperplasia
- PMID: 21341372
- PMCID: PMC4068126
- DOI: 10.1002/mabi.201000509
Poly(diol-co-citrate)s as novel elastomeric perivascular wraps for the reduction of neointimal hyperplasia
Abstract
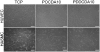
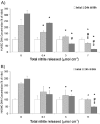
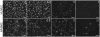
The synthesis of poly(diol-co-citrate) elastomers that are biocompatible with vascular cells and can modulate the kinetics of the NO release based on the diol of selection is reported. NO-mediated cytostatic or cytotoxic effects can be controlled depending on the NO dose and the exposure time. When implanted in vivo in a rat carotid artery injury model, these materials demonstrate a significant reduction of neointimal hyperplasia. This is the first report of a NO-releasing polymer fabricated in the form of an elastomeric perivascular wrap for the treatment of neointimal hyperplasia. These elastomers also show promise for other cardiovascular pathologies where NO-based therapies could be beneficial.
Copyright © 2011 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures






References
-
- Palmer RM, Ferrige AG, Moncada S. Nature. 1987;327:524. - PubMed
-
- Ignarro LJ, Byrns RE, Buga GM, Wood KS. Circ Res. 1987;61:866. - PubMed
-
- Lundberg JO, Weitzberg E, Gladwin MT. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008;7:156. - PubMed
-
- Napoli C, Ignarro LJ. Arch Pharm Res. 2009;32:1103. - PubMed
-
- Frost MC, Reynolds MM, Meyerhoff ME. Biomaterials. 2005;26:1685. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

