An improved coarse-grained model of solvation and the hydrophobic effect
- PMID: 21341830
- PMCID: PMC3077811
- DOI: 10.1063/1.3532939
An improved coarse-grained model of solvation and the hydrophobic effect
Abstract
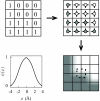
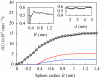
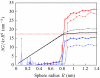
We present a coarse-grained lattice model of solvation thermodynamics and the hydrophobic effect that implements the ideas of Lum-Chandler-Weeks theory [J. Phys. Chem. B 134, 4570 (1999)] and improves upon previous lattice models based on it. Through comparison with molecular simulation, we show that our model captures the length-scale and curvature dependence of solvation free energies with near-quantitative accuracy and 2-3 orders of magnitude less computational effort, and further, correctly describes the large but rare solvent fluctuations that are involved in dewetting, vapor tube formation, and hydrophobic assembly. Our model is intermediate in detail and complexity between implicit-solvent models and explicit-water simulations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A self-consistent phase-field approach to implicit solvation of charged molecules with Poisson-Boltzmann electrostatics.J Chem Phys. 2015 Dec 28;143(24):243110. doi: 10.1063/1.4932336. J Chem Phys. 2015. PMID: 26723595 Free PMC article.
-
A coarse-grained model of DNA with explicit solvation by water and ions.J Phys Chem B. 2011 Jan 13;115(1):132-42. doi: 10.1021/jp107028n. Epub 2010 Dec 14. J Phys Chem B. 2011. PMID: 21155552 Free PMC article.
-
Self-assembling dipeptides: including solvent degrees of freedom in a coarse-grained model.Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2009 Mar 28;11(12):2068-76. doi: 10.1039/b818146m. Epub 2009 Feb 2. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2009. PMID: 19280017
-
Multiscale approaches and perspectives to modeling aqueous electrolytes and polyelectrolytes.Top Curr Chem. 2012;307:251-94. doi: 10.1007/128_2011_168. Top Curr Chem. 2012. PMID: 21630135 Review.
-
Advances in implicit models of water solvent to compute conformational free energy and molecular dynamics of proteins at constant pH.Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2011;85:281-322. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-386485-7.00008-9. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2011. PMID: 21920327 Review.
Cited by
-
Derivation and assessment of phase-shifted, disordered vector field models for frustrated solvent interactions.J Chem Phys. 2013 Feb 28;138(8):085103. doi: 10.1063/1.4792638. J Chem Phys. 2013. PMID: 23464179 Free PMC article.
-
Stochastic level-set variational implicit-solvent approach to solute-solvent interfacial fluctuations.J Chem Phys. 2016 Aug 7;145(5):054114. doi: 10.1063/1.4959971. J Chem Phys. 2016. PMID: 27497546 Free PMC article.
-
Spontaneous recovery of superhydrophobicity on nanotextured surfaces.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 May 17;113(20):5508-13. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1521753113. Epub 2016 May 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27140619 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced atomic pair-interaction design (RAPID) model for simulations of proteins.J Chem Phys. 2013 Feb 14;138(6):064102. doi: 10.1063/1.4790160. J Chem Phys. 2013. PMID: 23425456 Free PMC article.
-
Sitting at the edge: how biomolecules use hydrophobicity to tune their interactions and function.J Phys Chem B. 2012 Mar 1;116(8):2498-503. doi: 10.1021/jp2107523. Epub 2012 Feb 16. J Phys Chem B. 2012. PMID: 22235927 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tanford C., The Hydrophobic Effect: Formation of Micelles and Biological Membranes (Wiley, New York, 1973).
-
- Alberts B., Johnson A., Lewis J., Raff M., Roberts K., and Walter P., Molecular Biology of the Cell, 5th ed. (Garland Science, New York, 2007).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

