Adenosine modulates Toll-like receptor function: basic mechanisms and translational opportunities
- PMID: 21342073
- PMCID: PMC4052217
- DOI: 10.1586/eri.10.158
Adenosine modulates Toll-like receptor function: basic mechanisms and translational opportunities
Abstract
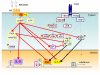
Adenosine is an endogenous purine metabolite whose concentration in human blood plasma rises from nanomolar to micromolar concentrations during the inflammatory process. Leukocytes express seven-transmembrane adenosine receptors whose engagement modulates Toll-like receptor-mediated cytokine responses, in part via modulation of intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate. Adenosine analogs are used clinically to treat arrhythmias and apnea of prematurity. Herein, we consider the potential of adenosine analogs as innate immune response modifiers to prevent and/or treat infection.
Figures

References
-
- Sitkovsky MV, Lukashev D, Apasov S, et al. Physiological control of immune response and inflammatory tissue damage by hypoxia-inducible factors and adenosine A2A receptors. Annual Review of Immunology. 2004;22:657–682. - PubMed
-
- Martin C, Leone M, Viviand X, Ayem ML, Guieu R. High adenosine plasma concentration as a prognostic index for outcome in patients with septic shock. Critical Care Medicine. 2000;28(9):3198–3202. - PubMed
-
- Hasko G, Cronstein BN. Adenosine: an endogenous regulator of innate immunity. Trends in Immunology. 2004;25(1):33–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
