Hyperbaric oxygen upregulates cochlear constitutive nitric oxide synthase
- PMID: 21342510
- PMCID: PMC3050772
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2202-12-21
Hyperbaric oxygen upregulates cochlear constitutive nitric oxide synthase
Abstract
Background: Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) is a known adjuvant for treating ischemia-related inner ear diseases. Controversies still exist in the role of HBOT in cochlear diseases. Few studies to date have investigated the cellular changes that occur in inner ears after HBOT. Nitric oxide, which is synthesized by nitric oxide synthase (NOS), is an important signaling molecule in cochlear physiology and pathology. Here we investigated the effects of hyperbaric oxygen on eardrum morphology, cochlear function and expression of NOS isoforms in cochlear substructures after repetitive HBOT in guinea pigs.
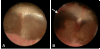
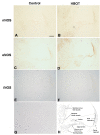
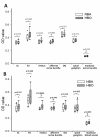
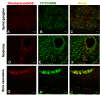
Results: Minor changes in the eardrum were observed after repetitive HBOT, which did not result in a significant hearing threshold shift by tone burst auditory brainstem responses. A differential effect of HBOT on the expression of NOS isoforms was identified. Upregulation of constitutive NOS (nNOS and eNOS) was found in the substructures of the cochlea after HBOT, but inducible NOS was not found in normal or HBOT animals, as shown by immunohistochemistry. There was no obvious DNA fragmentation present in this HBOT animal model.
Conclusions: The present evidence indicates that the customary HBOT protocol may increase constitutive NOS expression but such upregulation did not cause cell death in the treated cochlea. The cochlear morphology and auditory function are consequently not changed through the protocol.
Figures
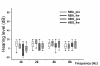
References
-
- Lamm K, Lamm C, Arnold W. Effect of isobaric oxygen versus hyperbaric oxygen on the normal and noise-damaged hypoxic and ischemic guinea pig inner ear. Adv Otorhinolaryngol. 1998;54:59–85. - PubMed
-
- Nakashima T, Fukuta S, Yanagita N. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for sudden deafness. Adv Otorhinolaryngol. 1998;54:100–109. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

