[Changes on mitochondrial DNA content in non-small cell lung cancer]
- PMID: 21342645
- PMCID: PMC5999772
- DOI: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2011.02.07
[Changes on mitochondrial DNA content in non-small cell lung cancer]
Abstract
Background and objective: It has been proven that the mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) mutations and content change were associated with increasing risk of tumorigenesis. MtDNA content is significantly reduced in most substantive tumors. The aim of this study is to demonstrate whether mtDNA content is positively associated with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) risk.
Methods: MtDNA content in 37 matched lung carcinoma and histologically adjacent normal lung tissue samples from patients were analyzed by fluorogenic 5-nuclease real-time PCR techniques.
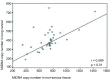
Results: The mean copy number of mtDNA in lung carcinoma tissue samples was statistically lower than that in adjacent histologically normal lung tissue samples (P < 0.001).
Conclusions: The change of mtDNA content may play an important role in NSCLC.
背景与目的: 已有的研究表明:线粒体DNA(mitochondrial DNA, mtDNA)突变和拷贝数的改变和肿瘤有着密切联系;大多数实体性肿瘤中mtDNA拷贝数有明显降低。本研究旨在探讨线粒体基因组含量的改变和原发性非小细胞肺癌(non-small cell lung cancer, NSCLC)的关系。
方法: 通过实时荧光定量PCR,对肺癌及相对应的癌旁肺组织mtDNA的含量进行精确定量(拷贝数/细胞)。
结果: 肺癌组织mtDNA的平均拷贝数/细胞为395±125,而相对应的正常肺组织为733±196,前者明显低于后者(P < 0.001)。肺癌mtDNA含量的改变与患者性别、年龄、是否吸烟及肿瘤的病理类型无关(P > 0.05)。
结论: mtDNA含量的改变与NSCLC的发生发展密切相关,同时也可能影响其治疗和预后。
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mitochondrial genome microsatellite instability and copy number alteration in lung carcinomas.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14(4):2393-9. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2013.14.4.2393. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013. PMID: 23725147
-
Prognostic value of mitochondrial DNA content and G10398A polymorphism in non-small cell lung cancer.Oncol Rep. 2013 Dec;30(6):3006-12. doi: 10.3892/or.2013.2783. Epub 2013 Oct 3. Oncol Rep. 2013. PMID: 24101028
-
Mitochondrial DNA 4977 BP deletion mutations in lung carcinoma.Indian J Cancer. 2006 Jan-Mar;43(1):20-5. doi: 10.4103/0019-509x.25771. Indian J Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16763358
-
Following mitochondrial footprints through a long mucosal path to lung cancer.PLoS One. 2009 Aug 6;4(8):e6533. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006533. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19657397 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial DNA in Lung Cancer.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1038:9-22. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-6674-0_2. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 29178066 Review.
Cited by
-
Lung cancer increases H2O2 concentration in the exhaled breath condensate, extent of mtDNA damage, and mtDNA copy number in buccal mucosa.Heliyon. 2020 Jun 28;6(6):e04303. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04303. eCollection 2020 Jun. Heliyon. 2020. PMID: 32637695 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical