Molecular modeling and in vivo imaging can identify successful flexible triazine dendrimer-based siRNA delivery systems
- PMID: 21342661
- PMCID: PMC3134114
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2011.02.016
Molecular modeling and in vivo imaging can identify successful flexible triazine dendrimer-based siRNA delivery systems
Abstract
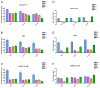
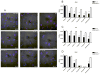
This study aimed to identify suitable siRNA delivery systems based on flexible generation 2-4 triazine dendrimers by correlating physico-chemical and biological in vitro and in vivo properties of the complexes with thermodynamic parameters calculated using molecular modeling. The siRNA binding properties of the dendrimers and PEI 25 kDa were simulated, binding and stability were measured in SYBR Gold assays, and hydrodynamic diameters, zeta potentials, and cytotoxicity were quantified. These parameters were compared with cellular uptake of the complexes and their ability to mediate RNAi. Radiolabeled complexes were administered intravenously, and pharmacokinetic profiles and biodistribution of these polyplexes were assessed both invasively and non-invasively. All flexible triazine dendrimers formed thermodynamically more stable complexes than PEI. While PEI and the generation 4 dendrimer interacted more superficially with siRNA, generation 2 and 3 virtually coalesced with siRNA, forming a tightly intertwined structure. These dendriplexes were therefore more efficiently charge-neutralized than PEI complexes, reducing agglomeration. This behavior was confirmed by results of hydrodynamic diameters (72.0 nm-153.5 nm) and zeta potentials (4.9 mV-21.8 mV in 10 mM HEPES) of the dendriplexes in comparison to PEI complexes (312.8 nm-480.0 nm and 13.7 mV-17.4 mV in 10 mM HEPES). All dendrimers, even generation 3 and 4, were less toxic than PEI. All dendriplexes were efficiently endocytosed and showed significant and specific luciferase knockdown in HeLa/Luc cells. Scintillation counting confirmed that the generation 2 triazine complexes showed more than twofold prolonged circulation times as a result of their good thermodynamic stability. Conversely, generation 3 complexes dissociated in vivo, and generation 4 complexes were captured by the reticulo-endothelial system due to their increased surface charge. Molecular modeling proves very valuable for rationalizing experimental parameters based on the dendrimers' structural properties. Non-invasive molecular imaging predicted the in vivo fate of the complexes. Therefore, both techniques effectively promote the rapid development of safe and efficient siRNA formulations that are stable in vivo.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


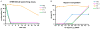

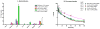
Similar articles
-
Triazine dendrimers as nonviral vectors for in vitro and in vivo RNAi: the effects of peripheral groups and core structure on biological activity.Mol Pharm. 2010 Aug 2;7(4):969-83. doi: 10.1021/mp100101s. Mol Pharm. 2010. PMID: 20524664 Free PMC article.
-
Triazine dendrimers as nonviral gene delivery systems: effects of molecular structure on biological activity.Bioconjug Chem. 2009 Sep;20(9):1799-806. doi: 10.1021/bc900243r. Bioconjug Chem. 2009. PMID: 19708683 Free PMC article.
-
Role of generation, architecture, pH and ionic strength on successful siRNA delivery and transfection by hybrid PPV-PAMAM dendrimers.Curr Med Chem. 2012;19(29):4929-41. doi: 10.2174/0929867311209024929. Curr Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22963640
-
How to study dendrimers and dendriplexes III. Biodistribution, pharmacokinetics and toxicity in vivo.J Control Release. 2014 May 10;181:40-52. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.02.021. Epub 2014 Mar 4. J Control Release. 2014. PMID: 24607663 Review.
-
Cationic Dendrimers for siRNA Delivery: An Overview of Methods for In Vitro/In Vivo Characterization.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2282:209-244. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1298-9_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33928579 Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of oligospermines architecture on their suitability for siRNA delivery.Biomacromolecules. 2014 Apr 14;15(4):1299-310. doi: 10.1021/bm401849d. Epub 2014 Mar 4. Biomacromolecules. 2014. PMID: 24552396 Free PMC article.
-
Radiolabeled Dendrimers for Nuclear Medicine Applications.Molecules. 2017 Aug 25;22(9):1350. doi: 10.3390/molecules22091350. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28841180 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multifunctional Neomycin-Triazine-Based Cationic Lipids for Gene Delivery with Antibacterial Properties.Bioconjug Chem. 2021 Apr 21;32(4):690-701. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.0c00616. Epub 2021 Jan 20. Bioconjug Chem. 2021. PMID: 33470802 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the blind spot of polycationic nanocarrier-based siRNA delivery.ACS Nano. 2012 Nov 27;6(11):9447-54. doi: 10.1021/nn301966r. Epub 2012 Oct 9. ACS Nano. 2012. PMID: 23036046 Free PMC article.
-
Can pulmonary RNA delivery improve our pandemic preparedness?J Control Release. 2022 May;345:549-556. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.03.039. Epub 2022 Mar 28. J Control Release. 2022. PMID: 35358609 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhou J, Wu J, Hafdi N, Behr JP, Erbacher P, Peng L. PAMAM dendrimers for efficient siRNA delivery and potent gene silencing. Chem Commun (Cambridge, U K) 2006:2362–2364. - PubMed
-
- Watanabe K, Harada-Shiba M, Suzuki A, Gokuden R, Kurihara R, Sugao Y, Mori T, Katayama Y, Niidome T. In vivo siRNA delivery with dendritic poly(L-lysine) for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia. Mol Biosyst. 2009;5:1306–1310. - PubMed
-
- Weber N, Ortega P, Clemente MI, Shcharbin D, Bryszewska M, de la Mata FJ, Gómez R, Muñoz-Fernández MA. Characterization of carbosilane dendrimers as effective carriers of siRNA to HIV-infected lymphocytes. J Control Release. 2008;132:55–64. - PubMed
-
- Merkel OM, Mintzer MA, Librizzi D, Samsonova O, Dicke T, Sproat B, Garn H, Barth PJ, Simanek EE, Kissel T. Triazine Dendrimers as Nonviral Vectors for in Vitro and in Vivo RNAi: The Effects of Peripheral Groups and Core Structure on Biological Activity. Mol Pharmaceutics. 2010;7:969–983. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

