RNA helicase p68 (DDX5) regulates tau exon 10 splicing by modulating a stem-loop structure at the 5' splice site
- PMID: 21343338
- PMCID: PMC3133221
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01149-10
RNA helicase p68 (DDX5) regulates tau exon 10 splicing by modulating a stem-loop structure at the 5' splice site
Abstract
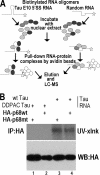
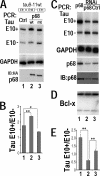
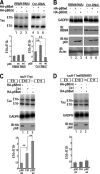
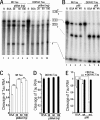
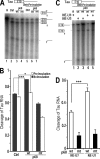
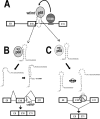
Regulation of tau exon 10 splicing plays an important role in tauopathy. One of the cis elements regulating tau alternative splicing is a stem-loop structure at the 5' splice site of tau exon 10. The RNA helicase(s) modulating this stem-loop structure was unknown. We searched for splicing regulators interacting with this stem-loop region using an RNA affinity pulldown-coupled mass spectrometry approach and identified DDX5/RNA helicase p68 as an activator of tau exon 10 splicing. The activity of p68 in stimulating tau exon 10 inclusion is dependent on RBM4, an intronic splicing activator. RNase H cleavage and U1 protection assays suggest that p68 promotes conformational change of the stem-loop structure, thereby increasing the access of U1snRNP to the 5' splice site of tau exon 10. This study reports the first RNA helicase interacting with a stem-loop structure at the splice site and regulating alternative splicing in a helicase-dependent manner. Our work uncovers a previously unknown function of p68 in regulating tau exon 10 splicing. Furthermore, our experiments reveal functional interaction between two splicing activators for tau exon 10, p68 binding at the stem-loop region and RBM4 interacting with the intronic splicing enhancer region.
Figures

References
-
- Andreadis A. 2005. Tau gene alternative splicing: expression patterns, regulation and modulation of function in normal brain and neurodegenerative diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1739:91–103 - PubMed
-
- Andreadis A. 2006. Misregulation of tau alternative splicing in neurodegeneration and dementia. Prog. Mol. Subcell. Biol. 44:89–107 - PubMed
-
- Andreadis A., Brown W. M., Kosik K. S. 1992. Structure and novel exons of the human tau gene. Biochemistry 31:10626–10633 - PubMed
-
- Avila J., Lim F., Moreno F., Belmonte C., Cuello A. C. 2002. Tau function and dysfunction in neurons: its role in neurodegenerative disorders. Mol. Neurobiol. 25:213–231 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
