Trypanosoma cruzi infection induces a global host cell response in cardiomyocytes
- PMID: 21343357
- PMCID: PMC3088143
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00643-10
Trypanosoma cruzi infection induces a global host cell response in cardiomyocytes
Erratum in
- Infect Immun. 2011 Aug;79(8):3471. Probst, Christian [corrected to Probst, Christian M]; Ozaki, L Shozo [corrected to Ozaki, Luiz Shozo]
Abstract
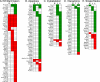
Chagas' disease, caused by the hemoflagellate protozoan Trypanosoma cruzi, affects millions of people in South and Central America. Chronic chagasic cardiomyopathy, the most devastating manifestation of this disease, occurs in approximately one-third of infected individuals. Events associated with the parasite's tropism for and invasion of cardiomyocytes have been the focus of intense investigation in recent years. In the present study, we use murine microarrays to investigate the cellular response caused by invasion of primary murine cardiomyocytes by T. cruzi trypomastigotes. These studies identified 353 murine genes that were differentially expressed during the early stages of invasion and infection of these cells. Genes associated with the immune response, inflammation, cytoskeleton organization, cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions, apoptosis, cell cycle, and oxidative stress are among those affected during the infection. Our data indicate that T. cruzi induces broad modulations of the host cell machinery in ways that provide insight into how the parasite survives, replicates, and persists in the infected host and ultimately defines the clinical outcome of the infection.
Figures



References
-
- Andrade S. G., Grimaud J. A., Stocker-Guerret S. 1989. Sequential changes of the connective matrix components of the myocardium (fibronectin and laminin) and evolution of cardiac fibrosis in mice infected with Trypanosoma cruzi. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 40:252–260 - PubMed
-
- Barbosa H. S., Meirelles M. N. 1993. The role of RCA-binding sites in the adhesion of Trypanosoma cruzi to heart muscle cells, as revealed by electron spectroscopic imaging. J. Submicrosc. Cytol. Pathol. 25:47–51 - PubMed
-
- Barbosa H. S., Meirelles M. N. 1992. Ultrastructural detection in vitro of WGA-, RCA I-, and ConA-binding sites involved in the invasion of heart muscle cells by Trypanosoma cruzi. Parasitol. Res. 78:404–409 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

