Mutant prevention concentration-based pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic indices as dosing targets for suppressing the enrichment of levofloxacin-resistant subpopulations of Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 21343454
- PMCID: PMC3088181
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00975-10
Mutant prevention concentration-based pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic indices as dosing targets for suppressing the enrichment of levofloxacin-resistant subpopulations of Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
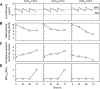
MIC- and mutant prevention concentration (MPC)-based pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) indices were compared for suitability as attainment targets for restricting amplification of levofloxacin-resistant mutant subpopulations. When three Staphylococcus aureus strains were examined with a hollow-fiber PK/PD model, area under the concentration-time curve over 24 h (AUC24)/MPC values of >25 and maximum concentration of drug in serum (Cmax)/MPC values of >2.2 predicted resistance outcome among different isolates with an interisolate kappa coefficient of 1. MIC-based mutant-restrictive PK/PD values varied >8-fold and exhibited only a moderate interisolate agreement (kappa coefficient of 0.5). Thus, MPC-based PK/PD indices are more suitable than MIC-based indices for predicting mutant-restricting fluoroquinolone doses when multiple bacterial isolates are considered.
Figures

References
-
- Ambrose P., Zoe-Powers A., Russo R., Jones D., Owens R. 2002. Utilizing pharmacodynamics and pharmacoeconomics in clinical and formulary decision making, p. 385–409 In Nightingale C., Murakawa T., Ambrose P. (ed.), Antimicrobial pharmacodynamics in theory and clinical practice. Marcel Dekker, New York, NY
-
- Baquero F., Negri M. 1997. Selective compartments for resistant microorganisms in antibiotic gradients. Bioessays 19:731–736 - PubMed
-
- Baquero F., Negri M., Morosini M., Blazquez J. 1997. The antibiotic selective process: concentration-specific amplification of low-level resistant populations. Ciba Found. Symp. 207:93–105 - PubMed
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. 2009. Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bacteria that grow aerobically: approved standard. CLSI publication M07-A8, vol. 29, no. 2 CLSI, Wayne, PA
-
- Craig W. 1998. Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic parameters: rationale for antibacterial dosing of mice and men. Clin. Infect. Dis. 26:1–12 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

