Expression of osteopontin coregulators in primary colorectal cancer and associated liver metastases
- PMID: 21343932
- PMCID: PMC3065273
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2011.33
Expression of osteopontin coregulators in primary colorectal cancer and associated liver metastases
Abstract
Background: A transcription regulatory complex (TRC) that includes Ets1, Ets2, PEA3 and β-catenin/T-cell factors regulates osteopontin (OPN) that is implicated in colorectal cancer (CRC) dissemination. The consistency of OPN transcriptional control between primary CRC and metastases is unclear. This study investigates expression and prognostic significance of the OPN-TRC in primary human CRC and associated colorectal liver metastases (CRLM).
Methods: Osteopontin-TRC factors were assayed by digital microscopy in 38 primary CRCs and matched CRLM specimens and assessed against clinical prognosis.
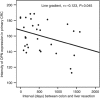
Results: In primary CRC, OPN expression intensity correlated with that of its co-activators, PEA3 (r=0.600; P<0.01), Ets1 (r=0.552; P<0.01), Ets2 (r=0.521; P<0.01) and had prognostic significance. Osteopontin intensity in primary CRC inversely correlated with the interval between diagnosis and resection of CRLM. Overall OPN intensity was lower in CRLM than primary CRC and correlations with co-activators were weaker, for example, Ets1 (P=0.047), PEA3 (P=0.022) or nonsignificant (Ets2). The ratio of OPN expression in CRLM vs primary CRC had prognostic significance.
Conclusion: This study supports transcriptional control of OPN by known coregulators in both primary and secondary CRC. Weaker associations in CRLM suggest involvement of other unknown factors possibly from the liver microenvironment or resulting from additional genetic or epigenetic changes that drive tumour metastatic capability in OPN transcriptional control.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Agrawal D, Chen T, Irby R, Quackenbush J, Chambers AF, Szabo M, Cantor A, Coppola D, Yeatman TJ (2002) Osteopontin identified as lead marker of colon cancer progression, using pooled sample expression profiling. J Natl Cancer Inst 94: 513–521 - PubMed
-
- El-Tanani M, Platt-Higgins A, Rudland PS, Campbell FC (2004) Ets gene PEA3 cooperates with beta-catenin-Lef-1 and c-Jun in regulation of osteopontin transcription. J Biol Chem 279: 20794–20806 - PubMed
-
- El-Tanani MK, Campbell FC, Kurisetty V, Jin D, McCann M, Rudland PS (2006) The regulation and role of osteopontin in malignant transformation and cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 17: 463–474 - PubMed
-
- El-Tanani MK, Jin D, Campbell FC, Johnston PG (2010) Interferon-induced transmembrane 3 binds osteopontin in vitro: expressed in vivo IFITM3 reduced OPN expression. Oncogene 29: 752–762 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

