Quantitative study of NPY-expressing GABAergic neurons and axons in rat spinal dorsal horn
- PMID: 21344400
- PMCID: PMC3258544
- DOI: 10.1002/cne.22570
Quantitative study of NPY-expressing GABAergic neurons and axons in rat spinal dorsal horn
Abstract
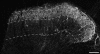
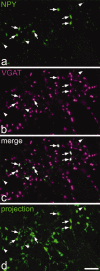
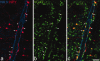
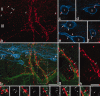
Between 25-40% of neurons in laminae I-III are GABAergic, and some of these express neuropeptide Y (NPY). We previously reported that NPY-immunoreactive axons form numerous synapses on lamina III projection neurons that possess the neurokinin 1 receptor (NK1r). The aims of this study were to determine the proportion of neurons and GABAergic boutons in this region that contain NPY, and to look for evidence that they selectively innervate different neuronal populations. We found that 4-6% of neurons in laminae I-III were NPY-immunoreactive and based on the proportions of neurons that are GABAergic, we estimate that NPY is expressed by 18% of inhibitory interneurons in laminae I-II and 9% of those in lamina III. GABAergic boutons were identified by the presence of the vesicular GABA transporter (VGAT) and NPY was found in 13-15% of VGAT-immunoreactive boutons in laminae I-II, and 5% of those in lamina III. For both the lamina III NK1r-immunoreactive projection neurons and protein kinase Cγ (PKCγ)-immunoreactive interneurons in lamina II, we found that around one-third of the VGAT boutons that contacted them were NPY-immunoreactive. However, based on differences in the sizes of these boutons and the strength of their NPY-immunoreactivity, we conclude that these originate from different populations of interneurons. Only 6% of VGAT boutons presynaptic to large lamina I projection neurons that lacked NK1rs contained NPY. These results show that NPY-containing neurons make up a considerable proportion of the inhibitory interneurons in laminae I-III, and that their axons preferentially target certain classes of dorsal horn neuron.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Galanin-immunoreactivity identifies a distinct population of inhibitory interneurons in laminae I-III of the rat spinal cord.Mol Pain. 2011 May 15;7:36. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-7-36. Mol Pain. 2011. PMID: 21569622 Free PMC article.
-
GABAergic neurons that contain neuropeptide Y selectively target cells with the neurokinin 1 receptor in laminae III and IV of the rat spinal cord.J Neurosci. 1999 Apr 1;19(7):2637-46. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-07-02637.1999. J Neurosci. 1999. PMID: 10087077 Free PMC article.
-
A quantitative study of neuronal nitric oxide synthase expression in laminae I-III of the rat spinal dorsal horn.Neuroscience. 2011 Sep 29;192(6-2):708-20. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.07.011. Epub 2011 Jul 14. Neuroscience. 2011. PMID: 21763759 Free PMC article.
-
Anatomy of primary afferents and projection neurones in the rat spinal dorsal horn with particular emphasis on substance P and the neurokinin 1 receptor.Exp Physiol. 2002 Mar;87(2):245-9. doi: 10.1113/eph8702351. Exp Physiol. 2002. PMID: 11856970 Review.
-
Petilla terminology: nomenclature of features of GABAergic interneurons of the cerebral cortex.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2008 Jul;9(7):557-68. doi: 10.1038/nrn2402. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18568015 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide expression analysis of Ptf1a- and Ascl1-deficient mice reveals new markers for distinct dorsal horn interneuron populations contributing to nociceptive reflex plasticity.J Neurosci. 2013 Apr 24;33(17):7299-307. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0491-13.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23616538 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying functional populations among the interneurons in laminae I-III of the spinal dorsal horn.Mol Pain. 2017 Jan;13:1744806917693003. doi: 10.1177/1744806917693003. Mol Pain. 2017. PMID: 28326935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New insights into the mechanisms behind mechanical itch.Exp Dermatol. 2020 Aug;29(8):680-686. doi: 10.1111/exd.14143. Epub 2020 Jul 19. Exp Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 32621303 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of Neuropeptide Y in Post-Incisional Nociception in Rats.Ann Neurosci. 2018 Dec;25(4):268-276. doi: 10.1159/000495130. Epub 2018 Dec 4. Ann Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 31000967 Free PMC article.
-
Galanin-immunoreactivity identifies a distinct population of inhibitory interneurons in laminae I-III of the rat spinal cord.Mol Pain. 2011 May 15;7:36. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-7-36. Mol Pain. 2011. PMID: 21569622 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Antal M, Polgár E, Chalmers J, Minson JB, Llewellyn-Smith I, Heizmann CW, Somogyi P. Different populations of parvalbumin- and calbindin-D28k-immunoreactive neurons contain GABA and accumulate 3H-D-aspartate in the dorsal horn of the rat spinal cord. J Comp Neurol. 1991;314:114–124. - PubMed
-
- Antal M, Petkó M, Polgár E, Heizmann CW, Storm-Mathisen J. Direct evidence of an extensive GABAergic innervation of the spinal dorsal horn by fibres descending from the rostral ventromedial medulla. Neuroscience. 1996;73:509–18. - PubMed
-
- Becker CM, Hoch W, Betz H. Sensitive immunoassay shows selective association of peripheral and integral membrane proteins of the inhibitory glycine receptor complex. J Neurochem. 1989;53:124–131. - PubMed
-
- Bjugn R, Gundersen HJ. Estimate of the total number of neurons and glial and endothelial cells in the rat spinal cord by means of the optical disector. J Comp Neurol. 1993;328:406–414. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

