Clinical phenotypes of a juvenile sibling pair carrying the fragile X premutation
- PMID: 21344625
- PMCID: PMC3568664
- DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.a.33446
Clinical phenotypes of a juvenile sibling pair carrying the fragile X premutation
Abstract
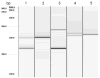
Individuals with alleles containing 55-200 CGG repeats in the fragile X mental retardation (FMR1) gene are premutation carriers. The premutation allele has been shown to lead to a number of types of clinical involvement, including shyness, anxiety, social deficits, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and executive function deficits. Some of these problems could be due to mild deficits of the fragile X protein (FMRP) and a possible developmental effect of the elevated FMR1 mRNA observed in carriers. In addition, two abnormal phenotypes specific to the premutation have been described. Primary ovarian insufficiency (FXPOI), defined by cessation of menses prior to age 40, occurs in 20% of females with the premutation. The other phenotype, fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome (FXTAS), affects some older adult premutation carriers. Premutation females typically have one expanded allele (≥55 CGG repeats) and one normal allele (≤54 CGG repeats). This study describes the cognitive, behavioral, and molecular profile of a female with two alleles in the premutation range (60 and 67 CGG repeats) in comparison to her brother with a similar premutation size (65 CGG repeats). Both exhibited high IQ scores, anxiety, and some physical features associated with fragile X syndrome. This comparison allows us to examine the effect of the premutation in this male-female pair while controlling for environmental and background genetic factors.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Allen EG, He W, Yadav-Shah M, Sherman SL. A study of the distributional characteristics of FMR1 transcript levels in 238 individuals. Hum Genet. 2004;114:439–447. - PubMed
-
- Aman MG, Singh N, Stewart A, Field CJ. The Aberrant Behavior Checklist: A behavior rating scale for the assessment of treatment effects. Am J Ment Defic. 1985;89:485–491. - PubMed
-
- Aziz M, Stathopulu E, Callias M, Taylor C, Turk J, Oostra B, Willemsen R, Patton M. Clinical features of boys with fragile X premutations and intermediate alleles. Am J Med Genet. 2003;121B:119–127. - PubMed
-
- Berry-Kravis E, Abrams L, Coffey SM, Hall DA, Greco C, Gane LW, Grigsby J, Bourgeois JA, Finucane B, Jacquemont S, Brunberg JA, Zhang L, Lin J, Tassone F, Hagerman PJ, Hagerman RJ, Leehey MA. Fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome: Clinical features, genetics, and testing guidelines. Mov Disord. 2007;22:2018–2030. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

