Perilipin deficiency and autosomal dominant partial lipodystrophy
- PMID: 21345103
- PMCID: PMC3773916
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1007487
Perilipin deficiency and autosomal dominant partial lipodystrophy
Abstract
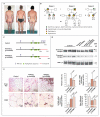
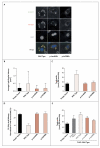
Perilipin is the most abundant adipocyte-specific protein that coats lipid droplets, and it is required for optimal lipid incorporation and release from the droplet. We identified two heterozygous frameshift mutations in the perilipin gene (PLIN1) in three families with partial lipodystrophy, severe dyslipidemia, and insulin-resistant diabetes. Subcutaneous fat from the patients was characterized by smaller-than-normal adipocytes, macrophage infiltration, and fibrosis. In contrast to wild-type perilipin, mutant forms of the protein failed to increase triglyceride accumulation when expressed heterologously in preadipocytes. These findings define a novel dominant form of inherited lipodystrophy and highlight the serious metabolic consequences of a primary defect in the formation of lipid droplets in adipose tissue.
Figures
References
-
- Frayn KN. Adipose tissue as a buffer for daily lipid flux. Diabetologia. 2002;45:1201–10. - PubMed
-
- Boutet E, El Mourabit H, Prot M, et al. Seipin deficiency alters fatty acid Delta9 desaturation and lipid droplet formation in Berardinelli-Seip congenital lipodystrophy. Biochimie. 2009;91:796–803. - PubMed
-
- Kim CA, Delépine M, Boutet E, et al. Association of a homozygous nonsense caveolin-1 mutation with Berardinelli-Seip congenital lipodystrophy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:1129–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
