Phenotypic and transcriptional analysis of the osmotic regulator OmpR in Yersinia pestis
- PMID: 21345178
- PMCID: PMC3050692
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2180-11-39
Phenotypic and transcriptional analysis of the osmotic regulator OmpR in Yersinia pestis
Abstract
Background: The osmotic regulator OmpR in Escherichia coli regulates differentially the expression of major porin proteins OmpF and OmpC. In Yersinia enterocolitica and Y. pseudotuberculosis, OmpR is required for both virulence and survival within macrophages. However, the phenotypic and regulatory roles of OmpR in Y. pestis are not yet fully understood.
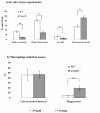
Results: Y. pestis OmpR is involved in building resistance against phagocytosis and controls the adaptation to various stressful conditions met in macrophages. The ompR mutation likely did not affect the virulence of Y. pestis strain 201 that was a human-avirulent enzootic strain. The microarray-based comparative transcriptome analysis disclosed a set of 224 genes whose expressions were affected by the ompR mutation, indicating the global regulatory role of OmpR in Y. pestis. Real-time RT-PCR or lacZ fusion reporter assay further validated 16 OmpR-dependent genes, for which OmpR consensus-like sequences were found within their upstream DNA regions. ompC, F, X, and R were up-regulated dramatically with the increase of medium osmolarity, which was mediated by OmpR occupying the target promoter regions in a tandem manner.
Conclusion: OmpR contributes to the resistance against phagocytosis or survival within macrophages, which is conserved in the pathogenic yersiniae. Y. pestis OmpR regulates ompC, F, X, and R directly through OmpR-promoter DNA association. There is an inducible expressions of the pore-forming proteins OmpF, C, and × at high osmolarity in Y. pestis, in contrast to the reciprocal regulation of them in E. coli. The main difference is that ompF expression is not repressed at high osmolarity in Y. pestis, which is likely due to the absence of a promoter-distal OmpR-binding site for ompF.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Regulatory effects of cAMP receptor protein (CRP) on porin genes and its own gene in Yersinia pestis.BMC Microbiol. 2011 Feb 23;11:40. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-11-40. BMC Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21345179 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional regulation of ompF2, an ompF paralogue, in Yersinia pestis.Can J Microbiol. 2011 Jun;57(6):468-75. doi: 10.1139/w11-028. Epub 2011 May 31. Can J Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21627465
-
Interaction of a transcriptional activator, OmpR, with reciprocally osmoregulated genes, ompF and ompC, of Escherichia coli.J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 25;261(36):17113-9. J Biol Chem. 1986. PMID: 3023382
-
Differential gene regulation in Yersinia pestis versus Yersinia pseudotuberculosis: effects of hypoxia and potential role of a plasmid regulator.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;603:131-44. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-72124-8_11. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 17966410 Review.
-
Yersinia Type III Secretion System Master Regulator LcrF.J Bacteriol. 2015 Dec 7;198(4):604-14. doi: 10.1128/JB.00686-15. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 26644429 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of regulatory sequences and expression analysis of OmpR gene under different stress conditions in the antarctic bacterium Psychrobacter sp. G.Curr Microbiol. 2013 Mar;66(3):259-65. doi: 10.1007/s00284-012-0266-5. Epub 2012 Nov 24. Curr Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23179079
-
Comparative transcriptomic analysis of the Burkholderia cepacia tyrosine kinase bceF mutant reveals a role in tolerance to stress, biofilm formation, and virulence.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013 May;79(9):3009-20. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00222-13. Epub 2013 Feb 22. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23435894 Free PMC article.
-
Vibrio cholerae OmpR Represses the ToxR Regulon in Response to Membrane Intercalating Agents That Are Prevalent in the Human Gastrointestinal Tract.Infect Immun. 2020 Feb 20;88(3):e00912-19. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00912-19. Print 2020 Feb 20. Infect Immun. 2020. PMID: 31871096 Free PMC article.
-
The Regulatory Circuit Underlying Downregulation of a Type III Secretion System in Yersinia enterocolitica by Transcription Factor OmpR.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 26;23(9):4758. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094758. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563149 Free PMC article.
-
The Regulator OmpR in Yersinia enterocolitica Participates in Iron Homeostasis by Modulating Fur Level and Affecting the Expression of Genes Involved in Iron Uptake.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 2;22(3):1475. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031475. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33540627 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Feng X, Oropeza R, Walthers D, Kenney LJ. OmpR phosphorylation and its role in signaling and pathogenesis. ASM News. 2003;69:390–395.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

