Prevalence and clinical associations of CXCR4-using HIV-1 among treatment-naive subtype C-infected women in Botswana
- PMID: 21346588
- PMCID: PMC3353541
- DOI: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e318214fe27
Prevalence and clinical associations of CXCR4-using HIV-1 among treatment-naive subtype C-infected women in Botswana
Abstract
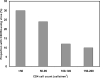
HIV-1 coreceptor use was determined using a phenotypic assay in plasma samples from treatment-naive women infected with subtype C virus who had CD4 cell counts below 200 cells/mm3. Of 148 women, 14.9% were infected with dual/mixed virus; the remainder had R5 virus. A greater proportion of women in the lowest CD4 cell count stratum had dual/mixed virus (P = 0.026); change in coreceptor use after antiretroviral therapy exposure was uncommon. CXCR4-using HIV-1 was less common in subtype C-infected women than reported in subtype B cohorts but was most prevalent in women with the lowest CD4 cell counts.
Figures
References
-
- Koot M, Keet IP, Vos AH, et al. Prognostic value of HIV-1 syncytium-inducing phenotype for rate of CD4+ cell depletion and progression to AIDS. Ann Intern Med. 1993 May 1;118(9):681–688. - PubMed
-
- Bozzette SA, McCutchan JA, Spector SA, et al. A cross-sectional comparison of persons with syncytium- and non-syncytium-inducing human immunodeficiency virus. J Infect Dis. 1993 Dec;168(6):1374–1379. - PubMed
-
- Richman DD, Bozzette SA. The impact of the syncytium-inducing phenotype of human immunodeficiency virus on disease progression. J Infect Dis. 1994 May;169(5):968–974. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials