Evaluation of an Ontology-anchored Natural Language-based Approach for Asserting Multi-scale Biomolecular Networks for Systems Medicine
- PMID: 21347135
- PMCID: PMC3041541
Evaluation of an Ontology-anchored Natural Language-based Approach for Asserting Multi-scale Biomolecular Networks for Systems Medicine
Abstract
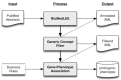
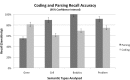
The ability to adequately and efficiently integrate unstructured, heterogeneous datasets, which are incumbent to systems biology and medicine, is one of the primary limitations to their comprehensive analysis. Natural language processing (NLP) and biomedical ontologies are automated methods for capturing, standardizing and integrating information across diverse sources, including narrative text. We have utilized the BioMedLEE NLP system to extract and encode, using standard ontologies (e.g., Cell Type Ontology, Mammalian Phenotype, Gene Ontology), biomolecular mechanisms and clinical phenotypes from the scientific literature. We subsequently applied semantic processing techniques to the structured BioMedLEE output to determine the relationships between these biomolecular and clinical phenotype concepts. We conducted an evaluation that shows an average precision and recall of BioMedLEE with respect to annotating phrases comprised of cell type, anatomy/disease, and gene/protein concepts were 86% and 78%, respectively. The precision of the asserted phenotype-molecular relationships was 75%.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PhenoGO: assigning phenotypic context to gene ontology annotations with natural language processing.Pac Symp Biocomput. 2006:64-75. Pac Symp Biocomput. 2006. PMID: 17094228 Free PMC article.
-
Automated ontology generation framework powered by linked biomedical ontologies for disease-drug domain.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2018 Oct;165:117-128. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2018.08.010. Epub 2018 Aug 16. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2018. PMID: 30337066
-
Extracting phenotypic information from the literature via natural language processing.Stud Health Technol Inform. 2004;107(Pt 2):758-62. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2004. PMID: 15360914
-
Natural language processing algorithms for mapping clinical text fragments onto ontology concepts: a systematic review and recommendations for future studies.J Biomed Semantics. 2020 Nov 16;11(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s13326-020-00231-z. J Biomed Semantics. 2020. PMID: 33198814 Free PMC article.
-
Natural language processing with machine learning methods to analyze unstructured patient-reported outcomes derived from electronic health records: A systematic review.Artif Intell Med. 2023 Dec;146:102701. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2023.102701. Epub 2023 Nov 1. Artif Intell Med. 2023. PMID: 38042599 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Price ND, et al. Systems Biology and the Emergence of Systems Medicine, in Genomic and Personalized Medicine. In: Willard HF, Ginsburg GS, editors. Elsevier; 2009. pp. 74–86.
-
- Joyce AR, Palsson BO. The model organism as a system: integrating ‘omics’ data sets. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7(3):198–210. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources