A rapid, inexpensive high throughput screen method for neurite outgrowth
- PMID: 21347208
- PMCID: PMC3040990
- DOI: 10.2174/1875397301004010074
A rapid, inexpensive high throughput screen method for neurite outgrowth
Abstract
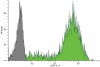
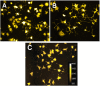
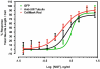
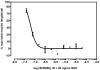
Neurite outgrowth assays are the most common phenotypic screen to assess chemical effects on neuronal cells. Current automated assays involve expensive equipment, lengthy sample preparation and handling, costly reagents and slow rates of data acquisition and analysis. We have developed a high throughput screen (HTS) for neurite outgrowth using a robust neuronal cell model coupled to fast and inexpensive visualization methods, reduced data volume and rapid data analysis. Neuroscreen-1 (NS-1) cell, a subclone of PC12, possessing rapid growth and enhanced sensitivity to NGF was used as a model neuron. This method reduces preparation time by using cells expressing GFP or native cells stained with HCS CellMask(™) Red in a multiplexed 30 min fixation and staining step. A 2x2 camera binning process reduced both image data files and analysis times by 75% and 60% respectively, compared to current protocols. In addition, eliminating autofocus steps during montage generation reduced data collection time. Pharmacological profiles for stimulation and inhibition of neurite outgrowth by NGF and SU6656 were comparable to current standard method utilizing immunofluorescence detection of tubulin. Potentiation of NGF-induced neurite outgrowth by members of a 1,120-member Prestwick compound library as assayed using this method identified six molecules, including etoposide, isoflupredone acetate, fludrocortisone acetate, thioguanosine, oxyphenbutazone and gibberellic acid, that more than doubled the neurite mass primed by 2 ng/ml NGF. This simple procedure represents an important routine approach in high throughput screening of large chemical libraries using the neurite outgrowth phenotype as a measure of the effects of chemical molecules on neuronal cells.
Keywords: NS-1; Nerve growth factor; PC12; SU6656.; high content screening; neurite outgrowth.
Figures
References
-
- Dragunow M. High-content analysis in neuroscience. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2008;9(10):779–88. - PubMed
-
- Thomas N. High-content screening: a decade of evolution. J Biomol Screen. 2010;15(1):1–9. - PubMed
-
- Das KP, Freudenrich TM, Mundy WR. Assessment of PC12 cell differentiation and neurite growth: a comparison of morphological and neurochemical measures. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2004;26(3):397–406. - PubMed
-
- Mitchell PJ, Hanson JC, Quets-Nguyen AT, Bergeron M, Smith RC. A quantitative method for analysis of in vitro neurite outgrowth. J Neurosci Methods. 2007;164(2):350–62. - PubMed
-
- Radio NM, Breier JM, Shafer TJ, Mundy WR. Assessment of chemical effects on neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells using high content screening. Toxicol Sci. 2008;105(1):106–18. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
