NF-κB potentiates caspase independent hydrogen peroxide induced cell death
- PMID: 21347231
- PMCID: PMC3039651
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016815
NF-κB potentiates caspase independent hydrogen peroxide induced cell death
Abstract
Background: The pro-survival activity of NF-κB in response to a variety of stimuli has been extensively characterized. Although there have been a few reports addressing the pro-cell death role of NF-κB, the precise mechanism of NF-κB's pro-cell death function still remains elusive.
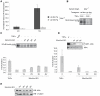
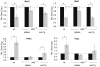
Methodology/principal findings: In the present study, we investigated the role of NF-κB in cell death induced by chronic insult with hydrogen peroxide (H(2)O(2)). Here, we show that NF-κB promotes H(2)O(2) induced caspase independent but PARP dependent fibroblast cell death. The pro-death activity of NF-κB is due to the DNA binding activity of RelA, which is induced through IKK- mediated IκBα degradation. NF-κB dependent pro-survival genes, Bcl-2 and XIAP, were significantly repressed, while NF-κB dependent pro-death genes, TNFα and Fas Ligand, were induced in response to H(2)O(2).
Conclusions/significance: We discovered an unexpected function of NF-κB, in that it potentiates chronic H(2)O(2) exposure induced cell death, and suggest that NF-κB mediates cell death through the repression of pro-survival genes and induction of pro-death genes. Since unremitting exposure of tissues to H(2)O(2) and other reactive oxygen species can lead to several degenerative disorders and diseases, our results have important implications for the use of NF-κB inhibitors in therapeutic drug design.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Role of caspases and NF-kappaB signaling in hydrogen peroxide- and superoxide-induced hepatocyte apoptosis.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2000 May;278(5):G693-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.2000.278.5.G693. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2000. PMID: 10801261
-
Resveratrol-induced apoptosis in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells involves a caspase-independent mechanism with downregulation of Bcl-2 and NF-kappaB.Int J Cancer. 2005 May 20;115(1):74-84. doi: 10.1002/ijc.20856. Int J Cancer. 2005. PMID: 15688415
-
IL-10 attenuates TNF-alpha-induced NF kappaB pathway activation and cardiomyocyte apoptosis.Cardiovasc Res. 2009 Apr 1;82(1):59-66. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvp040. Epub 2009 Jan 30. Cardiovasc Res. 2009. PMID: 19181934
-
Nuclear factor-kappaB translocation mediates double-stranded ribonucleic acid-induced NIT-1 beta-cell apoptosis and up-regulates caspase-12 and tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated ligand (TRAIL).Endocrinology. 2003 Oct;144(10):4616-25. doi: 10.1210/en.2003-0266. Epub 2003 Jun 26. Endocrinology. 2003. PMID: 12960048
-
Bcl-2 attenuation of oxidative cell death is associated with up-regulation of gamma-glutamylcysteine ligase via constitutive NF-kappaB activation.J Biol Chem. 2004 Sep 10;279(37):38779-86. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M406371200. Epub 2004 Jun 18. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15208316
Cited by
-
The diverse and complex roles of NF-κB subunits in cancer.Nat Rev Cancer. 2012 Jan 19;12(2):121-32. doi: 10.1038/nrc3204. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22257950 Review.
-
Signaling via the NFκB system.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2016 May;8(3):227-41. doi: 10.1002/wsbm.1331. Epub 2016 Mar 16. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2016. PMID: 26990581 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NFκB promotes oxidative stress-induced necrosis and ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting Nrf2-ARE pathway.Free Radic Biol Med. 2020 Nov 1;159:125-135. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.07.031. Epub 2020 Jul 31. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020. PMID: 32745764 Free PMC article.
-
Novel isothiacalothrixin B analogues exhibit cytotoxic activity on human colon cancer cells in vitro by inducing irreversible DNA damage.PLoS One. 2018 Sep 6;13(9):e0202903. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0202903. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30188913 Free PMC article.
-
IKK-β mediates hydrogen peroxide induced cell death through p85 S6K1.Cell Death Differ. 2013 Feb;20(2):248-58. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2012.115. Epub 2012 Sep 7. Cell Death Differ. 2013. PMID: 22955948 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cadenas E. Biochemistry of oxygen toxicity. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:79–110. - PubMed
-
- Valko M, Rhodes CJ, Moncol J, Izakovic M, Mazur M. Free radicals, metals and antioxidants in oxidative stress-induced cancer. Chem Biol Interact. 2006;160:1–40. - PubMed
-
- Behl C, Moosmann B. Oxidative nerve cell death in Alzheimer's disease and stroke: antioxidants as neuroprotective compounds. Biol Chem. 2002;383:521–536. - PubMed
-
- Nakamura Y, Romberger DJ, Tate L, Ertl RF, Kawamoto M, et al. Cigarette smoke inhibits lung fibroblast proliferation and chemotaxis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995;151:1497–1503. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

