Sodium-dependent vitamin C transporter 2 (SVCT2) expression and activity in brain capillary endothelial cells after transient ischemia in mice
- PMID: 21347255
- PMCID: PMC3037964
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017139
Sodium-dependent vitamin C transporter 2 (SVCT2) expression and activity in brain capillary endothelial cells after transient ischemia in mice
Abstract
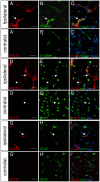
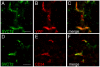
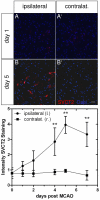
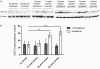
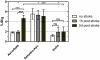
Expression and transport activity of Sodium-dependent Vitamin C Transporter 2 (SVCT2) was shown in various tissues and organs. Vitamin C was shown to be cerebroprotective in several animal models of stroke. Data on expression, localization and transport activity of SVCT2 after cerebral ischemia, however, has been scarce so far. Thus, we studied the expression of SVCT2 after middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) in mice by immunohistochemistry. We found an upregulation of SVCT2 after stroke. Co-stainings with Occludin, Von-Willebrand Factor and CD34 demonstrated localization of SVCT2 in brain capillary endothelial cells in the ischemic area after stroke. Time-course analyses of SVCT2 expression by immunohistochemistry and western blots showed upregulation in the subacute phase of 2-5 days. Radioactive uptake assays using (14)C-labelled ascorbic acid showed a significant increase of ascorbic acid uptake into the brain after stroke. Taken together, these results provide evidence for the expression and transport activity of SVCT2 in brain capillary endothelial cells after transient ischemia in mice. These results may lead to the development of novel neuroprotective strategies in stroke therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Dirnagl U, Iadecola C, Moskowitz MA. Pathobiology of ischaemic stroke: an integrated view. Trends Neurosci. 1999;22:391–397. - PubMed
-
- van Gijn J, Dennis MS. Issues and answers in stroke care. Lancet. 1998;352(Suppl 3):SIII23–27. - PubMed
-
- Heuschmann PU, Kolominsky-Rabas PL, Misselwitz B, Hermanek P, Leffmann C, et al. Predictors of in-hospital mortality and attributable risks of death after ischemic stroke: the German Stroke Registers Study Group. Arch Intern Med. 2004;164:1761–1768. - PubMed
-
- Rogalewski A, Schabitz WR. [Development of new stroke therapies: outlook for neuroprotective drugs]. Nervenarzt. 2008;79:218–224. - PubMed
-
- Huang J, May JM. Ascorbic acid protects SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells from apoptosis and death induced by beta-amyloid. Brain Res. 2006;1097:52–58. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

