The cGMP-dependent protein kinase II Is an inhibitory modulator of the hyperpolarization-activated HCN2 channel
- PMID: 21347269
- PMCID: PMC3038938
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017078
The cGMP-dependent protein kinase II Is an inhibitory modulator of the hyperpolarization-activated HCN2 channel
Abstract
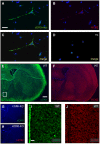
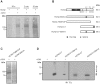
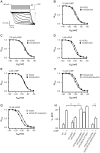
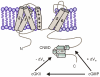
Opening of hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channels is facilitated by direct binding of cyclic nucleotides to a cyclic nucleotide-binding domain (CNBD) in the C-terminus. Here, we show for the first time that in the HCN2 channel cGMP can also exert an inhibitory effect on gating via cGMP-dependent protein kinase II (cGKII)-mediated phosphorylation. Using coimmunoprecipitation and immunohistochemistry we demonstrate that cGKII and HCN2 interact and colocalize with each other upon heterologous expression as well as in native mouse brain. We identify the proximal C-terminus of HCN2 as binding region of cGKII and show that cGKII phosphorylates HCN2 at a specific serine residue (S641) in the C-terminal end of the CNBD. The cGKII shifts the voltage-dependence of HCN2 activation to 2-5 mV more negative voltages and, hence, counteracts the stimulatory effect of cGMP on gating. The inhibitory cGMP effect can be either abolished by mutation of the phosphorylation site in HCN2 or by impairing the catalytic domain of cGKII. By contrast, the inhibitory effect is preserved in a HCN2 mutant carrying a CNBD deficient for cGMP binding. Our data suggest that bidirectional regulation of HCN2 gating by cGMP contributes to cellular fine-tuning of HCN channel activity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Regulation of hyperpolarization-activated HCN channel gating and cAMP modulation due to interactions of COOH terminus and core transmembrane regions.J Gen Physiol. 2001 Sep;118(3):237-50. doi: 10.1085/jgp.118.3.237. J Gen Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11524455 Free PMC article.
-
Salt bridges and gating in the COOH-terminal region of HCN2 and CNGA1 channels.J Gen Physiol. 2004 Dec;124(6):663-77. doi: 10.1085/jgp.200409178. J Gen Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15572346 Free PMC article.
-
The HCN domain is required for HCN channel cell-surface expression and couples voltage- and cAMP-dependent gating mechanisms.J Biol Chem. 2020 Jun 12;295(24):8164-8173. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.013281. Epub 2020 Apr 27. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32341127 Free PMC article.
-
Neurophysiology of HCN channels: from cellular functions to multiple regulations.Prog Neurobiol. 2014 Jan;112:1-23. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.10.001. Epub 2013 Oct 29. Prog Neurobiol. 2014. PMID: 24184323 Review.
-
Regulation of HCN Ion Channels by Non-canonical Cyclic Nucleotides.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2017;238:123-133. doi: 10.1007/164_2016_5006. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28181007 Review.
Cited by
-
Peripheral CCL2 induces inflammatory pain via regulation of Ih currents in small diameter DRG neurons.Front Mol Neurosci. 2023 Oct 4;16:1144614. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2023.1144614. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37860084 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring HCN channels as novel drug targets.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2011 Nov 18;10(12):903-14. doi: 10.1038/nrd3576. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2011. PMID: 22094868 Review.
-
Positive chronotropic action of HCN channel antagonism in human collecting lymphatic vessels.Physiol Rep. 2022 Aug;10(16):e15401. doi: 10.14814/phy2.15401. Physiol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35980021 Free PMC article.
-
Up-regulation of hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channel 3 (HCN3) by specific interaction with K+ channel tetramerization domain-containing protein 3 (KCTD3).J Biol Chem. 2013 Mar 15;288(11):7580-7589. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.434803. Epub 2013 Feb 4. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23382386 Free PMC article.
-
Xenon's Sedative Effect Is Mediated by Interaction with the Cyclic Nucleotide-Binding Domain (CNBD) of HCN2 Channels Expressed by Thalamocortical Neurons of the Ventrobasal Nucleus in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 11;24(10):8613. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108613. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37239964 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Craven KB, Zagotta WN. CNG and HCN channels: two peas, one pod. Annu Rev Physiol. 2006;68:375–401. - PubMed
-
- Robinson RB, Siegelbaum SA. Hyperpolarization-activated cation currents: from molecules to physiological function. Annu Rev Physiol. 2003;65:453–480. - PubMed
-
- DiFrancesco D. The role of the funny current in pacemaker activity. Circ Res. 2010;106:434–446. - PubMed
-
- Frere SG, Kuisle M, Luthi A. Regulation of recombinant and native hyperpolarization-activated cation channels. Mol Neurobiol. 2004;30:279–305. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

