Nocturnin expression is induced by fasting in the white adipose tissue of restricted fed mice
- PMID: 21347334
- PMCID: PMC3037405
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017051
Nocturnin expression is induced by fasting in the white adipose tissue of restricted fed mice
Abstract
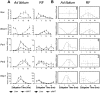
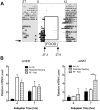
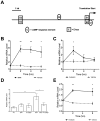
The relationship between circadian clocks and metabolism is intimate and complex and a number of recent studies have begun to reveal previously unknown effects of food and its temporal availability on the clock and the rhythmic transcriptome of peripheral tissues. Nocturnin, a circadian deadenylase, is expressed rhythmically in a wide variety of tissues, but we report here that Nocturnin expression is arrhythmic in epididymal white adipose tissue (eWAT) of mice housed in 12:12 LD with ad libitum access to food. However, Nocturnin expression becomes rhythmic in eWAT of mice placed on restricted feeding. We show here that Nocturnin's rhythmic expression pattern is not dependent upon feeding, nor is it acutely induced by feeding in the liver or eWAT of ad libitum fed mice. However, Nocturnin is acutely induced by the absence of the expected meal in eWAT of restricted fed mice. A rise in cAMP levels also induces Nocturnin expression, suggesting that Nocturnin's induction in eWAT by fasting is likely mediated through the same pathways that activate lipolysis. Therefore, this suggests that Nocturnin plays a role in linking nutrient sensing by the circadian clock to lipid mobilization in the adipocytes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Nocturnin: at the crossroads of clocks and metabolism.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Jul;23(7):326-33. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2012.03.007. Epub 2012 May 17. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2012. PMID: 22608110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-122 modulates the rhythmic expression profile of the circadian deadenylase Nocturnin in mouse liver.PLoS One. 2010 Jun 22;5(6):e11264. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011264. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20582318 Free PMC article.
-
Time-imposed daily restricted feeding induces rhythmic expression of Fgf21 in white adipose tissue of mice.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011 Aug 26;412(2):396-400. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.07.125. Epub 2011 Aug 3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011. PMID: 21835167
-
Loss of Nocturnin, a circadian deadenylase, confers resistance to hepatic steatosis and diet-induced obesity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Jun 5;104(23):9888-93. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0702448104. Epub 2007 May 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17517647 Free PMC article.
-
NOC out the fat: a short review of the circadian deadenylase Nocturnin.Ann Med. 2008;40(8):622-6. doi: 10.1080/07853890802084878. Ann Med. 2008. PMID: 18608124 Review.
Cited by
-
Dissociation between diurnal cycles in locomotor activity, feeding behavior and hepatic PERIOD2 expression in chronic alcohol-fed mice.Alcohol. 2015 Jun;49(4):399-408. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2015.03.005. Epub 2015 Apr 23. Alcohol. 2015. PMID: 25960184 Free PMC article.
-
Circadian genes, xBmal1 and xNocturnin, modulate the timing and differentiation of somites in Xenopus laevis.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 19;9(9):e108266. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0108266. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25238599 Free PMC article.
-
Nocturnin: at the crossroads of clocks and metabolism.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Jul;23(7):326-33. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2012.03.007. Epub 2012 May 17. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2012. PMID: 22608110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nocturnin regulates circadian trafficking of dietary lipid in intestinal enterocytes.Curr Biol. 2011 Aug 23;21(16):1347-55. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2011.07.018. Epub 2011 Aug 4. Curr Biol. 2011. PMID: 21820310 Free PMC article.
-
Daily rhythms in antennal protein and olfactory sensitivity in the malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae.Sci Rep. 2013;3:2494. doi: 10.1038/srep02494. Sci Rep. 2013. PMID: 23986098 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

