The obesity-associated polymorphisms FTO rs9939609 and MC4R rs17782313 and endometrial cancer risk in non-Hispanic white women
- PMID: 21347432
- PMCID: PMC3035652
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016756
The obesity-associated polymorphisms FTO rs9939609 and MC4R rs17782313 and endometrial cancer risk in non-Hispanic white women
Abstract
Overweight and obesity are strongly associated with endometrial cancer. Several independent genome-wide association studies recently identified two common polymorphisms, FTO rs9939609 and MC4R rs17782313, that are linked to increased body weight and obesity. We examined the association of FTO rs9939609 and MC4R rs17782313 with endometrial cancer risk in a pooled analysis of nine case-control studies within the Epidemiology of Endometrial Cancer Consortium (E2C2). This analysis included 3601 non-Hispanic white women with histologically-confirmed endometrial carcinoma and 5275 frequency-matched controls. Unconditional logistic regression models were used to assess the relation of FTO rs9939609 and MC4R rs17782313 genotypes to the risk of endometrial cancer. Among control women, both the FTO rs9939609 A and MC4R rs17782313 C alleles were associated with a 16% increased risk of being overweight (p = 0.001 and p = 0.004, respectively). In case-control analyses, carriers of the FTO rs9939609 AA genotype were at increased risk of endometrial carcinoma compared to women with the TT genotype [odds ratio (OR) = 1.17; 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.03-1.32, p = 0.01]. However, this association was no longer apparent after adjusting for body mass index (BMI), suggesting mediation of the gene-disease effect through body weight. The MC4R rs17782313 polymorphism was not related to endometrial cancer risk (per allele OR = 0.98; 95% CI: 0.91-1.06; p = 0.68). FTO rs9939609 is a susceptibility marker for white non-Hispanic women at higher risk of endometrial cancer. Although FTO rs9939609 alone might have limited clinical or public health significance for identifying women at high risk for endometrial cancer beyond that of excess body weight, further investigation of obesity-related genetic markers might help to identify the pathways that influence endometrial carcinogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

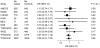
References
-
- Altekruse SF, Kosary CL, Krapcho M, Neyman N, Aminou R, et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2007, National Cancer Institute. Bethesda, MD. 2010 Available: http://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/corp.html. Accessed 2010 Aug 10.
-
- Kaaks R, Lukanova A, Kurzer MS. Obesity, endogenous hormones, and endometrial cancer risk: a synthetic review. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2002;11:1531–1543. - PubMed
-
- Kaaks R, Lukanova A. Energy balance and cancer: the role of insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I. Proc Nutr Soc. 2001;60:91–106. - PubMed
-
- Siiteri PK. Steroid hormones and endometrial cancer. Cancer Res. 1978;38:4360–4366. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CA54281/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA087538/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA134958/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- N01 PC35137/PC/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CAO82838/PHS HHS/United States
- N01CN67001/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HD 23166/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA 39779/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HD023166/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA054281/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01CA33619/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 PC035137/PC/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K05 CA092002/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K05 CA 92002/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA58598/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01-CA77596/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 CA 80636/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA87538/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA058598/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA 75977/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA105212/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA63464/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA063464/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA033619/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA 105212/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA134958/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 CA080636/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA38918/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA077596/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA063464/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA077398/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA054281/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States

