Filarial worms reduce Plasmodium infectivity in mosquitoes
- PMID: 21347449
- PMCID: PMC3035669
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0000963
Filarial worms reduce Plasmodium infectivity in mosquitoes
Abstract
Background: Co-occurrence of malaria and filarial worm parasites has been reported, but little is known about the interaction between filarial worm and malaria parasites with the same Anopheles vector. Herein, we present data evaluating the interaction between Wuchereria bancrofti and Anopheles punctulatus in Papua New Guinea (PNG). Our field studies in PNG demonstrated that An. punctulatus utilizes the melanization immune response as a natural mechanism of filarial worm resistance against invading W. bancrofti microfilariae. We then conducted laboratory studies utilizing the mosquitoes Armigeres subalbatus and Aedes aegypti and the parasites Brugia malayi, Brugia pahangi, Dirofilaria immitis, and Plasmodium gallinaceum to evaluate the hypothesis that immune activation and/or development by filarial worms negatively impact Plasmodium development in co-infected mosquitoes. Ar. subalbatus used in this study are natural vectors of P. gallinaceum and B. pahangi and they are naturally refractory to B. malayi (melanization-based refractoriness).
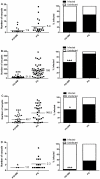
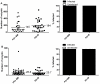
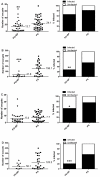
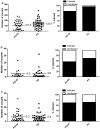
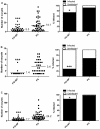
Methodology/principal findings: Mosquitoes were dissected and Plasmodium development was analyzed six days after blood feeding on either P. gallinaceum alone or after taking a bloodmeal containing both P. gallinaceum and B. malayi or a bloodmeal containing both P. gallinaceum and B. pahangi. There was a significant reduction in the prevalence and mean intensity of Plasmodium infections in two species of mosquito that had dual infections as compared to those mosquitoes that were infected with Plasmodium alone, and was independent of whether the mosquito had a melanization immune response to the filarial worm or not. However, there was no reduction in Plasmodium development when filarial worms were present in the bloodmeal (D. immitis) but midgut penetration was absent, suggesting that factors associated with penetration of the midgut by filarial worms likely are responsible for the observed reduction in malaria parasite infections.
Conclusions/significance: These results could have an impact on vector infection and transmission dynamics in areas where Anopheles transmit both parasites, i.e., the elimination of filarial worms in a co-endemic locale could enhance malaria transmission.
Conflict of interest statement
One of the authors, Dr. C.C. Chen, serves on the editorial board for PLoS NTDs.
Figures
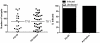
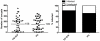
References
-
- Breman JG. The ears of the hippopotamus: manifestations, determinants, and estimates of the malaria burden. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2001;64:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Molyneux DH. Control of human parasitic diseases: Context and overview. Adv Parasitol. 2006;61:1–45. - PubMed
-
- Muturi EJ, Jacob BG, Kim CH, Mbogo CM, Novak RJ. Are coinfections of malaria and filariasis of any epidemiological significance? Parasitol Res. 2008;102:175–181. - PubMed
-
- Burkot TR, Molineaux L, Graves PM, Paru R, Battistutta D, et al. The prevalence of naturally acquired multiple infections of Wuchereria bancrofti and human malarias in anophelines. Parasitology 100 Pt. 1990;3:369–375. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

