Cardiac magnetic resonance visualizes acute and chronic myocardial injuries in myocarditis
- PMID: 21347598
- PMCID: PMC3288366
- DOI: 10.1007/s10554-011-9812-7
Cardiac magnetic resonance visualizes acute and chronic myocardial injuries in myocarditis
Abstract
Our objective was to evaluate the ability of CMR to visualize myocardial injuries over the course of myocarditis. We studied 42 patients (39 males, 3 females; age 37 ± 14 years) with myocarditis during the acute phase and after 12 ± 9 months. CMR included function analyses, T2-weighted imaging (T2 ratio), T1-weighted imaging before and after i.v. gadolinium injection (global relative enhancement; gRE), and late gadolinium enhancement (LGE). In the acute phase, the T2 ratio was elevated in 57%, gRE in 31%, and LGE was present in 64% of the patients. In 32 patients (76%) were any two (or more) out of three sequences abnormal. At follow-up, there was an increase in ejection fraction (57.4 ± 11.9% vs. 61.4 ± 7.6; P < 0.05) while both T2 ratio (2.04 ± 0.32 vs. 1.70 ± 0.28; P < 0.001) and gRE (4.07 ± 1.63 vs. 3.11 ± 1.22; P < 0.05) significantly decreased. The LGE persisted in 10 patients. Dilated cardiomyopathy was present in 3 patients and 4 patients received a defibrillator or a pacemaker. A comprehensive CMR approach is a useful tool to visualize myocardial tissue injuries over the course of myocarditis. CMR may help to differentiate acute from healed myocarditis, and add information for the differential diagnoses.
Figures
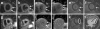

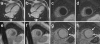
References
-
- Doolan A, Langlois N, Semsarian C. Causes of sudden cardiac death in young Australians. Med J Aust. 2004;180:110–112. - PubMed
-
- Kawai C. From myocarditis to cardiomyopathy: mechanisms of inflammation and cell death: learning from the past for the future. Circulation. 1999;99:1091–1100. - PubMed
-
- Masoudi FA, Magid DJ, Vinson DR, Tricomi AJ, Lyons EE, Crounse L, Ho PM, Peterson PN, Rumsfeld JS. Implications of the failure to identify high-risk electrocardiogram findings for the quality of care of patients with acute myocardial infarction: results of the Emergency Department Quality in Myocardial Infarction (EDQMI) study. Circulation. 2006;114:1565–1571. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.623652. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

