Real patient learning integrated in a preclinical block musculoskeletal disorders. Does it make a difference?
- PMID: 21347603
- PMCID: PMC3145092
- DOI: 10.1007/s10067-011-1708-3
Real patient learning integrated in a preclinical block musculoskeletal disorders. Does it make a difference?
Abstract
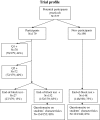
Although musculoskeletal disorders are the most common reason for general practitioner visits, training did not keep pace. Implementation of learning from patients with rheumatologic disorders linked together with the teaching of theoretical knowledge in the preclinical medical education might be an important step forward in the improvement of quality of care for these patients. The Leiden Medical School curriculum has implemented two non-obligatory real patient learning (RPL) practicals integrated within the preclinical block musculoskeletal disorders. This study investigates the educational effectiveness of the practicals, the expectations students have of RPL, and students' satisfaction. Participants' grades on the end-of-block test served as the test results of the educational effectiveness of the practicals and were compared with those of the non-participants. Qualitative data was collected by means of questionnaires generated by focus groups. The participants in practicals scored significantly higher at the end-of-block test. The expected effects of the contact with real patients concerned positive effects on cognition and skills. 'Contextualizing of the theory', 'better memorizing of clinical pictures', and 'understanding of the impact of the disease' were the most frequently mentioned effects of the practicals. Overall, the participants were (very) enthusiastic about this educational format. The RPL practicals integrated within a preclinical block musculoskeletal disorders are a valuable addition to the Leiden medical curriculum. This relatively limited intervention exhibits a strong effect on students' performance in tests. Future research should be directed towards the long-term effects of this intervention.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interactive seminars or small group tutorials in preclinical medical education: results of a randomized controlled trial.BMC Med Educ. 2010 Nov 13;10:79. doi: 10.1186/1472-6920-10-79. BMC Med Educ. 2010. PMID: 21073744 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Towards valid measures of self-directed clinical learning.Med Educ. 2003 Nov;37(11):983-91. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2923.2003.01677.x. Med Educ. 2003. PMID: 14629411
-
Flipped Learning: Can Rheumatology Lead the Shift in Medical Education?Curr Rheumatol Rev. 2019;15(1):67-73. doi: 10.2174/1573397114666180416170156. Curr Rheumatol Rev. 2019. PMID: 29663891
-
A global perspective on the challenges and opportunities in learning about rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases in undergraduate medical education : White paper by the World Forum on Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Diseases (WFRMD).Clin Rheumatol. 2020 Mar;39(3):627-642. doi: 10.1007/s10067-019-04544-y. Epub 2019 May 24. Clin Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 31127461 Review.
-
How should we be teaching our undergraduates?Ann Rheum Dis. 2000 Sep;59(9):662-7. doi: 10.1136/ard.59.9.662. Ann Rheum Dis. 2000. PMID: 10976077 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Role of active patient involvement in undergraduate medical education: a systematic review.BMJ Open. 2020 Jul 27;10(7):e037217. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-037217. BMJ Open. 2020. PMID: 32718925 Free PMC article.
-
Learning from patients' written feedback: medical students' experiences.Int J Med Educ. 2022 Jan 31;13:19-27. doi: 10.5116/ijme.61d5.8706. Int J Med Educ. 2022. PMID: 35108219 Free PMC article.
-
[Interactive electronic visualization formats in student teaching].HNO. 2024 May;72(5):341-349. doi: 10.1007/s00106-024-01436-9. Epub 2024 Feb 23. HNO. 2024. PMID: 38393668 Free PMC article. German.
-
A History of Musculoskeletal Medicine and Its Place and Progress in Undergraduate Medical Education.Med Sci Educ. 2023 Apr 25;33(3):777-790. doi: 10.1007/s40670-023-01782-3. eCollection 2023 Jun. Med Sci Educ. 2023. PMID: 37501799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Medical education trends for future physicians in the era of advanced technology and artificial intelligence: an integrative review.BMC Med Educ. 2019 Dec 11;19(1):460. doi: 10.1186/s12909-019-1891-5. BMC Med Educ. 2019. PMID: 31829208 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Badley EM, Rasooly I, Webster GK. Relative importance of musculoskeletal disorders as a cause of chronic health problems, disability, and health care utilization: findings from the 1990 Ontario Health Survey. J Rheumatol. 1994;21:505–514. - PubMed
-
- Dequeker J, Rasker H. High prevalence and impact of rheumatic diseases is not reflected in the medical curriculum: the ILAR Undergraduate Medical Education in Rheumatology (UMER) 2000 project. Together everybody achieves more. International League of Associations for Rheumatology. J Rheumatol. 1998;25:1037–1040. - PubMed
-
- Woolfe AD. Undergraduate medical education in rheumatology–aims. J Rheumatol Suppl. 1999;55:29–30. - PubMed
-
- Dequeker J. Undergraduate education in rheumatology: challenges for the millennium. J Rheumatol Suppl. 1999;55:3–5. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

