Stimulant effects of adenosine antagonists on operant behavior: differential actions of selective A2A and A1 antagonists
- PMID: 21347642
- PMCID: PMC3522121
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-011-2198-3
Stimulant effects of adenosine antagonists on operant behavior: differential actions of selective A2A and A1 antagonists
Abstract
Rationale: Adenosine A(2A) antagonists can reverse many of the behavioral effects of dopamine antagonists, including actions on instrumental behavior. However, little is known about the effects of selective adenosine antagonists on operant behavior when these drugs are administered alone.
Objective: The present studies were undertaken to investigate the potential for rate-dependent stimulant effects of both selective and nonselective adenosine antagonists.
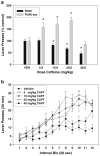
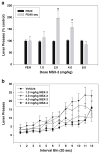
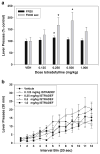
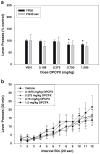
Methods: Six drugs were tested: two nonselective adenosine antagonists (caffeine and theophylline), two adenosine A(1) antagonists (DPCPX and CPT), and two adenosine A(2A) antagonists (istradefylline (KW6002) and MSX-3). Two schedules of reinforcement were employed; a fixed interval 240-s (FI-240 sec) schedule was used to generate low baseline rates of responding and a fixed ratio 20 (FR20) schedule generated high rates.
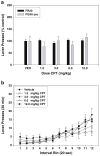
Results: Caffeine and theophylline produced rate-dependent effects on lever pressing, increasing responding on the FI-240 sec schedule but decreasing responding on the FR20 schedule. The A(2A) antagonists MSX-3 and istradefylline increased FI-240 sec lever pressing but did not suppress FR20 lever pressing in the dose range tested. In fact, there was a tendency for istradefylline to increase FR20 responding at a moderate dose. A(1) antagonists failed to increase lever pressing rate, but DPCPX decreased FR20 responding at higher doses.
Conclusions: These results suggest that adenosine A(2A) antagonists enhance operant response rates, but A(1) antagonists do not. The involvement of adenosine A(2A) receptors in regulating aspects of instrumental response output and behavioral activation may have implications for the treatment of effort-related psychiatric dysfunctions, such as psychomotor slowing and anergia in depression.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Differential actions of adenosine A1 and A2A antagonists on the effort-related effects of dopamine D2 antagonism.Behav Brain Res. 2009 Jul 19;201(1):216-22. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2009.02.021. Epub 2009 Mar 3. Behav Brain Res. 2009. PMID: 19428636 Free PMC article.
-
Adenosine A(2A) receptor antagonism reverses the effects of dopamine receptor antagonism on instrumental output and effort-related choice in the rat: implications for studies of psychomotor slowing.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2007 Apr;191(3):579-86. doi: 10.1007/s00213-006-0554-5. Epub 2006 Oct 27. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2007. PMID: 17072593
-
The adenosine A2A antagonist MSX-3 reverses the effects of the dopamine antagonist haloperidol on effort-related decision making in a T-maze cost/benefit procedure.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2009 May;204(1):103-12. doi: 10.1007/s00213-008-1441-z. Epub 2009 Jan 9. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2009. PMID: 19132351 Free PMC article.
-
Xanthines as adenosine receptor antagonists.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2011;(200):151-99. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-13443-2_6. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 20859796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nucleus accumbens neurotransmission and effort-related choice behavior in food motivation: effects of drugs acting on dopamine, adenosine, and muscarinic acetylcholine receptors.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2013 Nov;37(9 Pt A):2015-25. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2013.04.002. Epub 2013 Apr 10. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2013. PMID: 23583616 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of caffeine and its metabolite paraxanthine on intracranial self-stimulation in male rats.Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2015 Apr;23(2):71-80. doi: 10.1037/pha0000012. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25844631 Free PMC article.
-
The behavioral pharmacology of effort-related choice behavior: dopamine, adenosine and beyond.J Exp Anal Behav. 2012 Jan;97(1):125-46. doi: 10.1901/jeab.2012.97-125. J Exp Anal Behav. 2012. PMID: 22287808 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-term effects of THC exposure on reward learning and motivated behavior in adolescent and adult male rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2023 May;240(5):1151-1167. doi: 10.1007/s00213-023-06352-4. Epub 2023 Mar 18. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2023. PMID: 36933028 Free PMC article.
-
The VMAT-2 inhibitor tetrabenazine affects effort-related decision making in a progressive ratio/chow feeding choice task: reversal with antidepressant drugs.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 17;9(6):e99320. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0099320. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24937131 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular and Subjective Effects of the Novel Adenosine A(2A) Receptor Antagonist SYN115 in Cocaine Dependent Individuals.J Addict Res Ther. 2012 Mar 28;S1:009. doi: 10.4172/2155-6105.S1-009. J Addict Res Ther. 2012. PMID: 22905331 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ando K. Development of temporally spaced responding in relation to schedule value in rats. Jpn Psych Res. 1973;15(4):159–163.
-
- Antoniou K, Papadopoulou-Daifoti Z, Hyphantis T, Papathanasiou G, Bekris E, Marselos M, Panlilio L, Müller CE, Goldberg SR, Ferré S. A detailed behavioral analysis of the acute motor effects of caffeine in the rat: involvement of adenosine A1 and A2A receptors. Psychopharmacology. 2005;183(2):154–162. - PubMed
-
- Aubel B, Kayser V, Farré A, Hamon M, Bourgoin S. Evidence for adenosine- and serotonin-mediated antihyperalgesic effects of cizolirtine in rats suffering from diabetic neuropathy. Neuropharmacology. 2007;52:487–496. - PubMed
-
- Betz AJ, Vontell R, Valenta J, Worden L, Sink KS, Font L, Correa M, Sager TN, Salamone JD. Effects of the adenosine A 2A antagonist KW 6002 (istradefylline) on pimozide-induced oral tremor and striatal c-Fos expression: comparisons with the muscarinic antagonist tropicamide. Neuroscience. 2009;163(1):97–108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

