Multilocus variable-number tandem-repeat analysis, pulsed-field gel electrophoresis, and antimicrobial susceptibility patterns in discrimination of sporadic and outbreak-related strains of Yersinia enterocolitica
- PMID: 21349206
- PMCID: PMC3053224
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2180-11-42
Multilocus variable-number tandem-repeat analysis, pulsed-field gel electrophoresis, and antimicrobial susceptibility patterns in discrimination of sporadic and outbreak-related strains of Yersinia enterocolitica
Abstract
Background: We assessed the potential of multilocus variable-number tandem-repeat analysis (MLVA), pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE), and antimicrobial susceptibility testing for discriminating 104 sporadic and outbreak-related Yersinia enterocolitica (YE) bio/serotype 3-4/O:3 and 2/O:9 isolates. MLVA using six VNTR markers was performed in two separate multiplex PCRs, and the fluorescently labeled PCR products were accurately sized on an automated DNA sequencer.
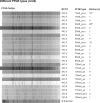
Results: MLVA discriminated 82 sporadic YE 3-4/O:3 and 2/O:9 strains into 77 types, whereas PFGE with the restriction enzyme NotI discriminated the strains into 23 different PFGE pulsotypes. The discriminatory index for a sporadic strain was 0.862 for PFGE and 0.999 for MLVA. MLVA confirmed that a foodborne outbreak in the city of Kotka, Finland in 2003 had been caused by a multiresistant YE 4/O:3 strain that was distinctly different from those of epidemiologically unrelated strains with an identical PFGE pulsotype. The multiresistance of Y. enterocolitica strains (19% of the sporadic strains) correlated significantly (p = 0.002) with travel abroad. All of the multiresistant Y. enterocolitica strains belonged to four PFGE pulsotypes that did not contain any susceptible strains. Resistance to nalidixic acid was related to changes in codons 83 or 87 that stemmed from mutations in the gyrA gene. The conjugation experiments demonstrated that resistance to CHL, STR, and SUL was carried by a conjugative plasmid.
Conclusions: MLVA using six loci had better discriminatory power than PFGE with the NotI enzyme. MLVA was also a less labor-intensive method than PFGE and the results were easier to analyze. The conjugation experiments demonstrated that a resistance plasmid can easily be transferred between Y. enterocolitica strains. Antimicrobial multiresistance of Y. enterocolitica strains was significantly associated with travel abroad.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genotyping of outbreak-associated and sporadic Yersinia pseudotuberculosis strains by novel multilocus variable-number tandem repeat analysis (MLVA).J Microbiol Methods. 2013 Nov;95(2):245-50. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2013.09.007. Epub 2013 Sep 17. J Microbiol Methods. 2013. PMID: 24050949
-
Characterization of Salmonella Typhimurium isolates from domestically acquired infections in Finland by phage typing, antimicrobial susceptibility testing, PFGE and MLVA.BMC Microbiol. 2015 Jul 2;15:131. doi: 10.1186/s12866-015-0467-8. BMC Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26129826 Free PMC article.
-
Multilocus variable-number tandem repeat analysis for molecular typing and phylogenetic analysis of Shigella flexneri.BMC Microbiol. 2009 Dec 31;9:278. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-9-278. BMC Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 20042119 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid and Simple Universal Escherichia coli Genotyping Method Based on Multiple-Locus Variable-Number Tandem-Repeat Analysis Using Single-Tube Multiplex PCR and Standard Gel Electrophoresis.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019 Mar 6;85(6):e02812-18. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02812-18. Print 2019 Mar 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30610078 Free PMC article.
-
Development and application of MLVA methods as a tool for inter-laboratory surveillance.Euro Surveill. 2013 Aug 29;18(35):20565. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.es2013.18.35.20565. Euro Surveill. 2013. PMID: 24008231 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Yersinia enterocolitica strains associated with human infections in Switzerland 2001-2010.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2012 Jul;31(7):1543-50. doi: 10.1007/s10096-011-1476-7. Epub 2011 Nov 10. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2012. PMID: 22071910
-
First Description of a Yersinia pseudotuberculosis Clonal Outbreak in France, Confirmed Using a New Core Genome Multilocus Sequence Typing Method.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Aug 31;10(4):e0114522. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01145-22. Epub 2022 Jul 6. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35863020 Free PMC article.
-
An outbreak of Yersinia enterocolitica in a captive colony of African green monkeys (Chlorocebus aethiops sabaeus) in the Caribbean.Comp Med. 2013 Oct;63(5):439-44. Comp Med. 2013. PMID: 24210021 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity of Yersinia enterocolitica isolated from pigs in a French slaughterhouse over 2 years.Microbiologyopen. 2019 Jun;8(6):e00751. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.751. Epub 2018 Oct 22. Microbiologyopen. 2019. PMID: 30350482 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Multiple-Locus Variable-Number Tandem Repeat Analysis Profiles of Enteropathogenic Yersinia spp. Obtained from Humans, Domestic Pigs, Wild Boars, Rodents, Pork and Dog Food.Animals (Basel). 2023 Sep 29;13(19):3055. doi: 10.3390/ani13193055. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37835661 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

