Exhaustive T-cell repertoire sequencing of human peripheral blood samples reveals signatures of antigen selection and a directly measured repertoire size of at least 1 million clonotypes
- PMID: 21349924
- PMCID: PMC3083096
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.115428.110
Exhaustive T-cell repertoire sequencing of human peripheral blood samples reveals signatures of antigen selection and a directly measured repertoire size of at least 1 million clonotypes
Abstract
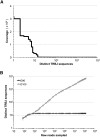
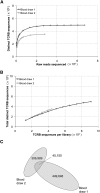
Massively parallel sequencing is a useful approach for characterizing T-cell receptor diversity. However, immune receptors are extraordinarily difficult sequencing targets because any given receptor variant may be present in very low abundance and may differ legitimately by only a single nucleotide. We show that the sensitivity of sequence-based repertoire profiling is limited by both sequencing depth and sequencing accuracy. At two timepoints, 1 wk apart, we isolated bulk PBMC plus naïve (CD45RA+/CD45RO-) and memory (CD45RA-/CD45RO+) T-cell subsets from a healthy donor. From T-cell receptor beta chain (TCRB) mRNA we constructed and sequenced multiple libraries to obtain a total of 1.7 billion paired sequence reads. The sequencing error rate was determined empirically and used to inform a high stringency data filtering procedure. The error filtered data yielded 1,061,522 distinct TCRB nucleotide sequences from this subject which establishes a new, directly measured, lower limit on individual T-cell repertoire size and provides a useful reference set of sequences for repertoire analysis. TCRB nucleotide sequences obtained from two additional donors were compared to those from the first donor and revealed limited sharing (up to 1.1%) of nucleotide sequences among donors, but substantially higher sharing (up to 14.2%) of inferred amino acid sequences. For each donor, shared amino acid sequences were encoded by a much larger diversity of nucleotide sequences than were unshared amino acid sequences. We also observed a highly statistically significant association between numbers of shared sequences and shared HLA class I alleles.
Figures

References
-
- Arstila TP, Casrouge A, Baron V, Even J, Kanellopoulos J, Kourilsky P 1999. A direct estimate of the human T cell receptor diversity. Science 286: 958–961 - PubMed
-
- Bassing CH, Swat W, Alt FW 2002. The mechanism and regulation of chromosomal V(D)J recombination. Cell 109(Suppl): S45–S55 - PubMed
-
- Cereb N, Maye P, Lee S, Kong Y, Yang SY 1995. Locus-specific amplification of HLA class I genes from genomic DNA: Locus-specific sequences in the first and third introns of HLA-A, -B, and -C alleles. Tissue Antigens 45: 1–11 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
