Vandetanib restores head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells' sensitivity to cisplatin and radiation in vivo and in vitro
- PMID: 21350000
- PMCID: PMC3074405
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2120
Vandetanib restores head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells' sensitivity to cisplatin and radiation in vivo and in vitro
Abstract
Purpose: We investigated whether vandetanib, an inhibitor of the tyrosine kinase activities of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 (VEGFR-2), epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), and rearranged during transfection (RET), could augment the antitumor activity of radiation with or without cisplatin in preclinical in vitro and in vivo models of human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC).
Experimental design: OSC-19 and HN5 HNSCC cells that were cisplatin and radioresistant were treated with vandetanib, cisplatin, and radiation alone or in combination in vitro and in vivo using an orthotopic nude mouse model. Treatment effects were assessed using clonogenic survival assay, tumor volume, bioluminescence imaging, tumor growth delay, survival, microvessel density, tumor and endothelial cell apoptosis, and EGFR and Akt phosphorylation data.
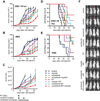
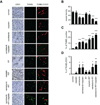
Results: Vandetanib plus cisplatin radiosensitized HNSCC cells in vitro and in vivo. The combination treatment with vandetanib, cisplatin, and radiation was superior to the rest of treatments (including the double combinations) in antitumoral effects, prolonging survival, decreasing cervical lymph node metastases in vivo. It also increased both tumor and tumor-associated endothelial cell apoptosis and decreased microvessel density in vivo. An analysis of tumor growth delay data revealed that vandetanib plus cisplatin enhanced radioresponse in vivo. All vandetanib-containing treatments inhibited EGFR and Akt phosphorylation in vitro and in vivo.
Conclusion: The addition of vandetanib to combination therapy with cisplatin and radiation was able to effectively overcome cisplatin and radioresistance in in vitro and in vivo models of HNSCC. Further study of this regimen in clinical trials may be warranted.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Targeted molecular therapy of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma with the tyrosine kinase inhibitor vandetanib in a mouse model.Head Neck. 2011 Mar;33(3):349-58. doi: 10.1002/hed.21455. Head Neck. 2011. PMID: 20629091 Free PMC article.
-
Dose scheduling of the dual VEGFR and EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor vandetanib (ZD6474, Zactima) in combination with radiotherapy in EGFR-positive and EGFR-null human head and neck tumor xenografts.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2008 Feb;61(2):179-88. doi: 10.1007/s00280-007-0460-5. Epub 2007 Mar 29. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 17393165
-
Telaglenastat as an alternative to cisplatin as a radiosensitizer in the treatment of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Cancer Lett. 2024 Dec 1;606:217320. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2024.217320. Epub 2024 Nov 1. Cancer Lett. 2024. PMID: 39489210
-
Epidermal growth factor receptors as a target for cancer treatment: the emerging role of IMC-C225 in the treatment of lung and head and neck cancers.Semin Oncol. 2002 Feb;29(1 Suppl 4):27-36. doi: 10.1053/sonc.2002.31525. Semin Oncol. 2002. PMID: 11894011 Review.
-
Improving the Predictive Value of Preclinical Studies in Support of Radiotherapy Clinical Trials.Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Jul 1;22(13):3138-47. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-0069. Epub 2016 May 6. Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27154913 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting the Extra-Cellular Matrix-Tumor Cell Crosstalk for Anti-Cancer Therapy: Emerging Alternatives to Integrin Inhibitors.Front Oncol. 2020 Jul 22;10:1231. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01231. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32793493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preclinical evaluation of the combination of mTOR and proteasome inhibitors with radiotherapy in malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors.J Neurooncol. 2014 May;118(1):83-92. doi: 10.1007/s11060-014-1422-5. Epub 2014 Mar 26. J Neurooncol. 2014. PMID: 24668609 Free PMC article.
-
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2/neu as a novel therapeutic target in sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma.Head Neck. 2016 Apr;38 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):E1926-34. doi: 10.1002/hed.24350. Epub 2016 Jan 11. Head Neck. 2016. PMID: 26752332 Free PMC article.
-
A novel extracellular drug conjugate significantly inhibits head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Oral Oncol. 2013 Oct;49(10):991-7. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2013.07.006. Epub 2013 Aug 3. Oral Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23920309 Free PMC article.
-
On-demand intracellular amplification of chemoradiation with cancer-specific plasmonic nanobubbles.Nat Med. 2014 Jul;20(7):778-784. doi: 10.1038/nm.3484. Epub 2014 Jun 1. Nat Med. 2014. PMID: 24880615 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer Statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010 - PubMed
-
- Goldberg HI, Lockwood SA, Wyatt SW, Crossett LS. Trends and differentials in mortality from cancers of the oral cavity and pharynx in the United States, 1973–1987. Cancer. 1994;74:565–572. - PubMed
-
- Sano D, Myers JN. Metastasis of squamous cell carcinoma of the oral tongue. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2007;26:645–662. - PubMed
-
- Forastiere AA. Is there a new role for induction chemotherapy in the treatment of head and neck cancer? J Natl Cancer Inst. 2004;96:1647–1649. - PubMed
-
- Adelstein DJ, Li Y, Adams GL, et al. An intergroup phase III comparison of standard radiation therapy and two schedules of concurrent chemoradiotherapy in patients with unresectable squamous cell head and neck cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:92–98. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

