Plasma biomarkers that reflect determinants of matrix composition identify the presence of left ventricular hypertrophy and diastolic heart failure
- PMID: 21350055
- PMCID: PMC4071931
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.110.958199
Plasma biomarkers that reflect determinants of matrix composition identify the presence of left ventricular hypertrophy and diastolic heart failure
Abstract
Background: Chronic pressure overload (such as arterial hypertension) may cause left ventricular (LV) remodeling, alterations in cardiac function, and the development of diastolic heart failure. Changes in the composition of the myocardial extracellular matrix may contribute to the development of pressure-overload-induced LV remodeling. We hypothesized that a specific pattern of plasma biomarker expression that reflected changes in these pathophysiological mechanisms would have diagnostic application to identify (1) patients who have development of LV hypertrophy (LVH) and (2) patients with LVH who have development of diastolic heart failure.
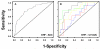
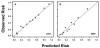
Methods and results: Plasma concentration of 17 biomarkers (matrix metalloproteinase [MMP]-1, -2, -3, -7, -8, and -9; tissue inhibitors -1, -2, -3, and -4; N-terminal propeptide of brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP); cardiotrophin; osteopontin; soluble receptor for advanced glycation end products; collagen I teleopeptide; collagen I NT-proBNP; and collagen III N-terminal propetide [PIIINP]), an echocardiogram, and 6-minute hall walk were performed on 241 referent control subjects, 144 patients with LVH but no evidence of heart failure, and 61 patients with LVH and diastolic heart failure (DHF). A plasma multibiomarker panel consisting of increased MMP-7, MMP-9, TIMP-1, PIIINP, and NT-proBNP predicted the presence of LVH with an area under the curve of 0.80. A plasma multibiomarker panel consisting of increased MMP-2, TIMP-4, PIIINP, and decreased MMP-8 predicted the presence of DHF with an area under the curve of 0.79. These multibiomarker panels performed better than any single biomarker including NT-proBNP and better than using clinical covariates alone (area under the curve, 0.73 for LVH and 0.68 for DHF).
Conclusions: Plasma biomarkers reflecting changes in extracellular matrix fibrillar collagen homeostasis, combined into a multibiomarker panel, have discriminative value in identifying the presence of structural remodeling (LVH) and clinical disease (DHF).
Figures

References
-
- Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman WC, Green LA, Izzo JL, Jr, Jones DW, Materson BJ, Oparil S, Wright JT, Jr, Roccella EJ, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure; National High Blood Pressure Education Program Coordinating Committee The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure: the JNC 7 report. JAMA. 2003;289:2560–72. - PubMed
-
- Vasan RS, Beiser A, Seshadri S, Larson MG, Kannel WB, D’Agostino RB, Levy D. Residual lifetime risk for developing hypertension in middle-aged women and men: The Framingham Heart Study. JAMA. 2002;287:1003–10. - PubMed
-
- Levy D, Larson MG, Vasan RS, Kannel WB, Ho KKL. The progression from hypertension to congestive heart failure. JAMA. 1996;275:1557–1562. - PubMed
-
- Lloyd-Jones DM, Larson MG, Leip EP, Beiser A, D’Agostino RB, Kannel WB, Murabito JM, Vasan RS, Benjamin EJ, Levy D. Lifetime risk for developing congestive heart failure. The Framingham Study. Circulation. 2002;106:3068–3072. - PubMed
-
- Verdecchia P, Schillaci G, Borgioni C, Ciucci A, Gattobigio R, Zampi I, Porcellati C. Prognostic value of a new electrocardiographic method for diagnosis of left ventricular hypertrophy in essential hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1998;31:383–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

