Beta3-integrin mediates satellite cell differentiation in regenerating mouse muscle
- PMID: 21350117
- PMCID: PMC3101029
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.10-170449
Beta3-integrin mediates satellite cell differentiation in regenerating mouse muscle
Abstract
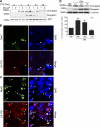
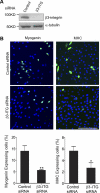
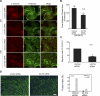
Skeletal muscle satellite cells can sense various forms of environmental cues and initiate coordinated signaling that activates myogenesis. Although this process involves cellular membrane receptor integrins, the role of integrins in myogenesis is not well defined. Here, we report a regulatory role of β3-integrin, which was previously thought not expressed in muscle, in the initiation of satellite cell differentiation. Undetected in normal muscle, β3-integrin expression in mouse hindlimb muscles is induced dramatically from 1 to 3 d after injury by cardiotoxin. The source of β3-integrin expression is found to be activated satellite cells. Proliferating C2C12 myoblasts also express β3-integrin, which is further up-regulated transiently on differentiation. Knockdown of β3-integrin expression attenuates Rac1 activity, impairs myogenic gene expression, and disrupts focal adhesion formation and actin organization, resulting in impaired myoblast migration and myotube formation. Conversely, overexpression of constitutively active Rac1 rescues myotube formation. In addition, a β3-integrin-neutralizing antibody similarly blocked myotube formation. Comparing with wild-type littermates, myogenic gene expression and muscle regeneration in cardiotoxin-injured β3-integrin-null mice are impaired, as indicated by depressed expression of myogenic markers and morphological disparities. Thus, β3-integrin is a mediator of satellite cell differentiation in regenerating muscle.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The role of PDIA3 in myogenesis during muscle regeneration.Exp Mol Med. 2020 Jan;52(1):105-117. doi: 10.1038/s12276-019-0368-2. Epub 2020 Jan 20. Exp Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 31956274 Free PMC article.
-
Role of integrin-β3 protein in macrophage polarization and regeneration of injured muscle.J Biol Chem. 2012 Feb 24;287(9):6177-86. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.292649. Epub 2011 Dec 30. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22210777 Free PMC article.
-
Teashirt-3, a novel regulator of muscle differentiation, associates with BRG1-associated factor 57 (BAF57) to inhibit myogenin gene expression.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jul 1;286(26):23498-510. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.206003. Epub 2011 May 4. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21543328 Free PMC article.
-
Focal adhesion kinase signaling regulates the expression of caveolin 3 and beta1 integrin, genes essential for normal myoblast fusion.Mol Biol Cell. 2009 Jul;20(14):3422-35. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e09-02-0175. Epub 2009 May 20. Mol Biol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19458188 Free PMC article.
-
PKCθ signaling is required for myoblast fusion by regulating the expression of caveolin-3 and β1D integrin upstream focal adhesion kinase.Mol Biol Cell. 2011 Apr 15;22(8):1409-19. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E10-10-0821. Epub 2011 Feb 23. Mol Biol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21346196 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Synthetic matrix enhances transplanted satellite cell engraftment in dystrophic and aged skeletal muscle with comorbid trauma.Sci Adv. 2018 Aug 15;4(8):eaar4008. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aar4008. eCollection 2018 Aug. Sci Adv. 2018. PMID: 30116776 Free PMC article.
-
Multifaceted Interweaving Between Extracellular Matrix, Insulin Resistance, and Skeletal Muscle.Cells. 2018 Sep 22;7(10):148. doi: 10.3390/cells7100148. Cells. 2018. PMID: 30249008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Costameric integrin and sarcoglycan protein levels are altered in a Drosophila model for Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2H.Mol Biol Cell. 2021 Feb 1;32(3):260-273. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E20-07-0453. Epub 2020 Dec 9. Mol Biol Cell. 2021. PMID: 33296226 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of RGD functionalization and stiffness modulation of polyelectrolyte multilayer films on muscle cell differentiation.Acta Biomater. 2013 May;9(5):6468-80. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2012.12.015. Epub 2012 Dec 20. Acta Biomater. 2013. PMID: 23261924 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicle-derived miRNAs improve stem cell-based therapeutic approaches in muscle wasting conditions.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 14;13:977617. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.977617. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36451814 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Charge S. B., Rudnicki M. A. (2004) Cellular and molecular regulation of muscle regeneration. Physiol. Rev. 84, 209–238 - PubMed
-
- Wagers A. J., Conboy I. M. (2005) Cellular and molecular signatures of muscle regeneration: current concepts and controversies in adult myogenesis. Cell 122, 659–667 - PubMed
-
- Hynes R. O. (1992) Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell 69, 11–25 - PubMed
-
- Silver F. H., Siperko L. M. (2003) Mechanosensing and mechanochemical transduction: how is mechanical energy sensed and converted into chemical energy in an extracellular matrix? Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 31, 255–331 - PubMed
-
- Clemmons D. R., Maile L. A. (2005) Interaction between insulin-like growth factor-I receptor and alphaVbeta3 integrin linked signaling pathways: cellular responses to changes in multiple signaling inputs. Mol. Endocrinol. 19, 1–11 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

