Upregulation of P-glycoprotein by probiotics in intestinal epithelial cells and in the dextran sulfate sodium model of colitis in mice
- PMID: 21350189
- PMCID: PMC3119110
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00027.2011
Upregulation of P-glycoprotein by probiotics in intestinal epithelial cells and in the dextran sulfate sodium model of colitis in mice
Abstract
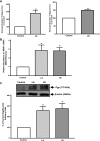
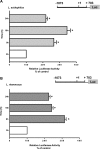
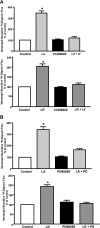
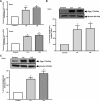
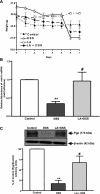
P-glycoprotein (P-gp) mediates efflux of xenobiotics and bacterial toxins from the intestinal mucosa into the lumen. Dysregulation of P-gp has been implicated in inflammatory bowel disease. Certain probiotics have been shown to be effective in treating inflammatory bowel disease. However, direct effects of probiotics on P-gp are not known. Current studies examined the effects of Lactobacilli on P-gp function and expression in intestinal epithelial cells. Caco-2 monolayers and a mouse model of dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis were utilized. P-gp activity was measured as verapamil-sensitive [(3)H]digoxin transepithelial flux. Multidrug resistant 1 (MDR1)/P-gp expression was measured by real-time quantitative PCR and immunoblotting. Culture supernatant (CS; 1:10 or 1:50, 24 h) of Lactobacillus acidophilus or Lactobacillus rhamnosus treatment of differentiated Caco-2 monolayers (21 days postplating) increased (∼3-fold) MDR1/P-gp mRNA and protein levels. L. acidophilus or L. rhamnosus CS stimulated P-gp activity (∼2-fold, P < 0.05) via phosphoinositide 3-kinase and ERK1/2 MAPK pathways. In mice, L. acidophilus or L. rhamnosus treatment (3 × 10(9) colony-forming units) increased mdr1a/P-gp mRNA and protein expression in the ileum and colon (2- to 3-fold). In the dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis model (3% DSS in drinking water for 7 days), the degree of colitis as judged by histological damage and myeloperoxidase activity was reduced by L. acidophilus. L. acidophilus treatment to DSS-treated mice blocked the reduced expression of mdr1a/P-gp mRNA and protein in the distal colon. These findings suggest that Lactobacilli or their soluble factors stimulate P-gp expression and function under normal and inflammatory conditions. These data provide insights into a novel mechanism involving P-gp upregulation in beneficial effects of probiotics in intestinal inflammatory disorders.
Figures
References
-
- Blokzijl H, Vander Borght S, Bok LI, Libbrecht L, Geuken M, van den Heuvel FA, Dijkstra G, Roskams TA, Moshage H, Jansen PL, Faber KN. Decreased P-glycoprotein (P-gp/MDR1) expression in inflamed human intestinal epithelium is independent of PXR protein levels. Inflamm Bowel Dis 13: 710–720, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Bradford M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72: 248–254, 1976 - PubMed
-
- Broekaert IJ, Nanthakumar NN, Walker WA. Secreted probiotic factors ameliorate enteropathogenic infection in zinc-deficient human Caco2 and T84 cell lines. Pediatr Res 62: 139–144, 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

