Pumilio Puf domain RNA-binding proteins in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 21350339
- PMCID: PMC3142416
- DOI: 10.4161/psb.6.3.14380
Pumilio Puf domain RNA-binding proteins in Arabidopsis
Abstract
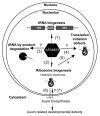
Pumilio proteins are a class of RNA-binding proteins harboring Puf domains (or PUM-HD; Pumilio-Homology Domain), named after the founding members, Pumilio (from Drosophila melanogaster) and FBF (Fem-3 mRNA-Binding Factor from Caenorhabditis elegans). The domains contain multiple tandem repeats each of which recognizes one RNA base and is comprised of 35-39 amino acids. Puf domain proteins have been reported in organisms ranging from single-celled yeast to higher multicellular eukaryotes, such as humans and plants. In yeast and animals, they are involved in a variety of posttranscriptional RNA metabolism including RNA decay, RNA transport, rRNA processing and translational repression. However, their roles in plants are largely unknown. Recently, we have characterized the first member of the Puf family of RNA-binding proteins, APUM23, in Arabidopsis. Here, we discuss and summarize the diverse roles and targets of Puf proteins previously reported in other organisms and then highlight the potential regulatory roles of Puf proteins in Arabidopsis, using our recent study as an example.
Figures

References
-
- Spassov DS, Jurecic R. The PUF family of RNAbinding proteins: does evolutionarily conserved structure equal conserved function? IUBMB Life. 2003;55:359–366. - PubMed
-
- Wang X, McLachlan J, Zamore PD, Hall TM. Modular recognition of RNA by a human pumilio-homology domain. Cell. 2002;110:501–512. - PubMed
-
- Goldstrohm AC, Hook BA, Seay DJ, Wickens M. PUF proteins bind Pop2p to regulate messenger RNAs. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2006;13:533–539. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
