Incidence of extramedullary disease in patients with multiple myeloma in the era of novel therapy, and the activity of pomalidomide on extramedullary myeloma
- PMID: 21350560
- PMCID: PMC3736849
- DOI: 10.1038/leu.2011.29
Incidence of extramedullary disease in patients with multiple myeloma in the era of novel therapy, and the activity of pomalidomide on extramedullary myeloma
Abstract
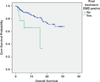
We studied 174 consecutive patients with relapsed refractory multiple myeloma (MM) enrolled on a phase II clinical trial of pomalidomide plus low-dose dexamethasone at Mayo Clinic. Extramedullary disease (EMD) was present at the time of trial entry in 7.5% (13 of 174 patients). The rate of EMD in the first 3 years following diagnosis of MM was 3%. The response of EMD to pomalidomide plus low-dose dexamethasone included two complete and two partial responses among the 13 patients (response rate, 31%). Overall survival measured from trial entry was significantly shorter for patients with treatment-emergent EMD compared with those who did not have EMD, (median 16 months versus not reached, P=0.002).
Conflict of interest statement
The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Madan S, Kumar S. Review: extramedullary disease in multiple myeloma. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. 2009;7:802–804. - PubMed
-
- Varettoni M, Corso A, Pica G, Mangiacavalli S, Pascutto C, Lazzarino M. Incidence, presenting features and outcome of extramedullary disease in multiple myeloma: a longitudinal study on 1003 consecutive patients. Ann Oncol. 2009;21:325–330. - PubMed
-
- Kyle RA, Gertz MA, Witzig TE, Lust J, Lacy M, Dispenzieri A, et al. Review of 1,027 patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma. Mayo Clinic Proc. 2003;78:21–33. - PubMed
-
- Blade J, Perales M, Rosinol L, Tuset M, Montoto S, Esteve J, et al. Thalidomide in multiple myeloma: lack of response of soft-tissue plasmacytomas [see comment] Br J Haematol. 2001;113:422–424. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical